


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 26-10-2020
Date: 18-5-2016
Date: 12-12-2016
|
Oscillating Systems
One form of motion pervades physical processes oscillatory motion. We have just mentioned sound and light. Sound, as is well known, is produced by oscillating, or vibrating, systems guitar strings, drum skins, air oscillating in a flute or trumpet, the vocal cords which produce our voices and so on. Similarly, as will be discussed, light is simply the manifestation of oscillating electric and magnetic fields (in conjunction, referred to as electromagnetic fields). For that matter so are radio waves and x-rays. Of course oscillations vary not only in the nature of the oscillating systems but also in their frequency and their amplitude. Frequency is the number of complete oscillations that take place in a unit of time; it is defined as the number of oscillations per second. It is different frequencies that account for the different notes obtained from musical instruments. Similarly the different frequencies of oscillating electromagnetic fields correspond to different colours of light, radio waves and x-rays. Amplitude is a measure of how large an oscillation is and, for example, with sound or light determines how loud or how bright they are respectively. In considering the behaviour of solid matter, oscillations of the component atoms will again be found to be a key feature in achieving understanding. It is therefore important to explore just a little further the nature of oscillations and the simplest system to consider is what is referred to as the simple pendulum. Such a pendulum is illustrated in figure 1.1. It consists essentially of a small weight (bob) suspended by a thread oscillating between two
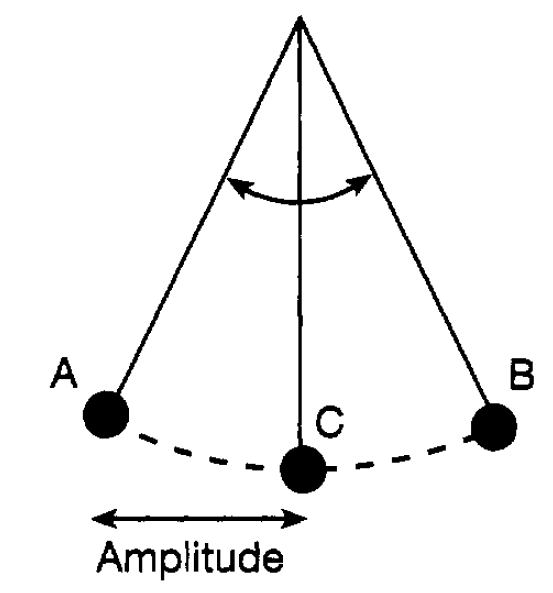
Figure 1.1: The simple pendulum,
points A and B. The amplitude of the oscillation is simply the maximum distance the bob moves from the centre (C) of its motion and the frequency is the number of complete oscillations it makes in a second where, by a complete oscillation is meant, for example, motion starting from A and returning to A. The nature of the motion of the pendulum is easily understood in terms of the energy involved. At rest, the bob of the pendulum is at the point C. If it is now set into motion by a sideways push it moves, say, to A where it instantaneously comes to rest. It then accelerates under the force of gravity towards C where it has maximum speed and then slows down as it moves towards B where it again comes instantaneously to rest. It then repeats this motion but in the opposite direction and so on, if there is no friction, ad infinitum. At C it has maximum kinetic energy whilst at A and B it has zero kinetic energy, being stationary, but has maximum potential energy (equal to the kinetic energy at C). At intermediate positions the bob has some kinetic and some potential energy, but the total is always the same reflecting the law of conservation of energy. The variation of the potential energy with position is shown in figure 1.2. Point C is the natural position of rest (equilibrium) of the bob where it has its lowest potential energy and, in an evocative way, it is usual to speak of it as being at the bottom of a ‘potential well’. Energy is needed to move the bob to A or B and the situation is analogous to a person confined in a valley needing
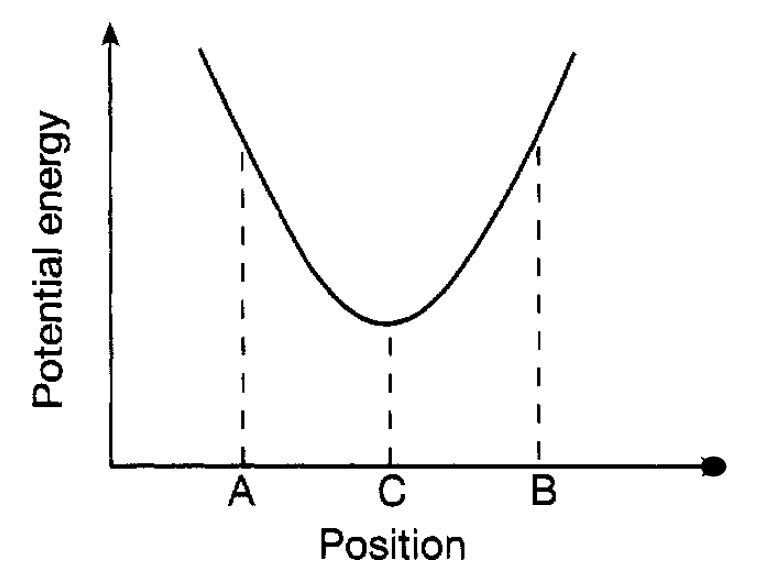
Figure 1.2 The potential energy curve for a pendulum bob.
energy to climb up the sides. Of course, this discussion of a pendulum refers to the ideal situation existing if there were no air resistance it needs to be suspended in a vacuum. In reality, due to the air resistance, after being set in motion and then left to itself, the amplitude will gradually decrease as the pendulum hands over energy, as it moves, to the surrounding air molecules. Eventually, when all of the energy initially given to it has been absorbed by the surrounding air, it comes to rest at C. It is interesting to note that, provided the amplitude is not too large, the frequency of oscillation is independent of the size of the amplitude the increased speed of travel for a larger amplitude oscillation exactly compensates for the necessarily increased
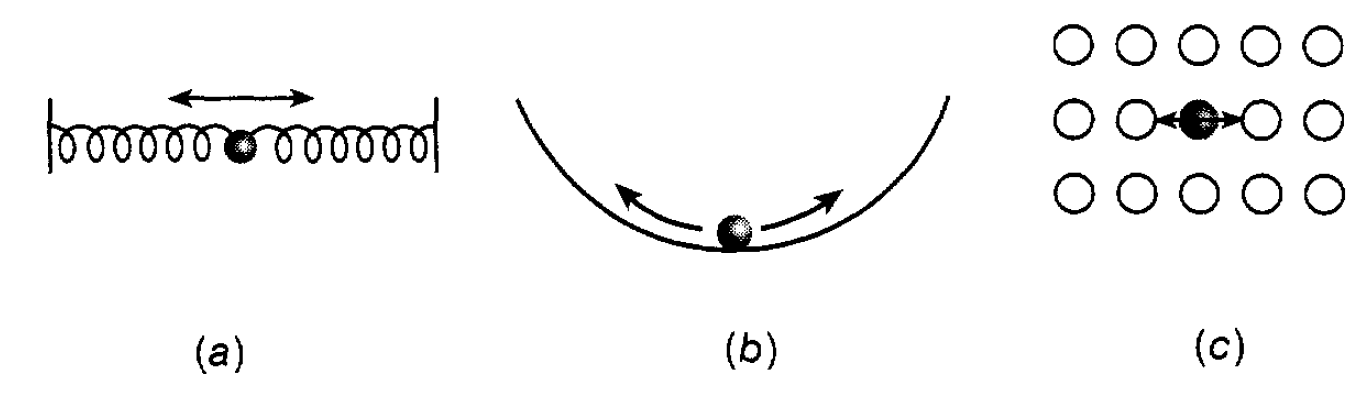
Figure 1.3: Systems in simple harmonic motion. (a) Oscillating springs. (b) A ball bearing oscillating in a bowl. (c) An oscillating atom.
distance of travel. Such motion is universally referred to as simple harmonic motion and will be frequently encountered as we plunge deeper and deeper into physics. It is exhibited (see figure 1.3), for example, by a bob held between two springs and by a ball bearing rolling in the bottom of a curved bowl through to an atom held in place by surrounding atoms in a solid.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|