


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 23-2-2022
Date: 5-1-2016
Date: 23-2-2022
|
Astronomical measurement began before recorded history. Early astronomy was concerned mainly with establishing the calendar, which was of great importance to the first agricultural societies, who needed to accurately predict when to plant and harvest crops. The earliest collection of astronomical data that has been found dates from the Babylonian Empire of the fifth century B.C.E. Astronomical records were kept on clay tablets and consisted of intricate sequences of numbers that were used to calculate the daily positions of the planets.
Much of what is known of early Greek mathematics was written almost a thousand years after the events occurred. A work known as the Summary of Proclus, written in the fifth century, refers to a lost history of geometry that was written around 350 B.C.E. by Eudemus, a pupil of Aristotle. Eudemus credited Thales with being the first geometer. According to this account, Thales was able to calculate the distance of a ship from the shore, although it is unclear how he determined this figure. However, the following is one possible method.
Let the ship be at a point S and the observers on the shore be at points A and B. They measure the angles through which they turn when first looking at each other and then at the ship, angle ABS and angle BAS. One observer now walks along the shore, counting the paces taken until reaching the other observer; this is the baseline of the observations. The distance to the ship can now be estimated by constructing a scale drawing. The longer the baseline, the more accurately the ship’s distance can be estimated.
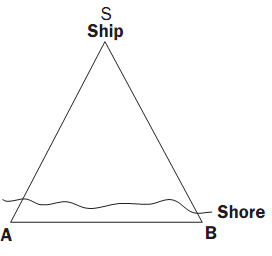
Early Attempts to Measure Astronomical Distances
A long baseline is needed to measure astronomical distances. On March 14, 190 B.C.E. there was an eclipse of the Sun, and Hipparchus had the angle of inclination of the Moon at the time of the eclipse measured at Istanbul and Alexandria. From this data he was able to estimate that the Moon’s distance was 71 times Earth’s radius. Given the imprecise instruments used in these measurements, this is fairly close to today’s accepted value of 59 Earth radii.
The challenge then was to calculate the size of Earth’s radius. Earth’s radius was first measured by Eratosthenes of Cyrene (276–195 B.C.E.), who read that at the summer solstice there was no shadow at midday in Syene. By observing the angle of a vertical pole at Alexandria on the same day and at the same time, Eratosthenes was able to estimate that the angle that the line of longitude from Alexandria to Syene subtended was an angle of just over 7°, which was 1/50 of the circumference of Earth. Using the best available measurement for the distance between the two towns, Eratosthenes obtained a circumference for Earth of about 29,000 miles, as compared to our current average circumference of around 25,000 miles. Once the circumference was determined, the radius was easily calculated. Although the Greeks did not have telescopes, or other instruments that would let them measure angles accurately, their measurements were fairly accurate.
Modern Astronomical Measurement
The modern period of astronomical measurement began with Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543), who reestablished the proposal that Earth is a sphere, an idea first advanced by Pythagoras in the sixth century B.C.E.He also concluded that Earth spun west to east and it was this movement that gave the effect of making the Sun, Moon, and stars rise in the east and set in the west. Copernicus placed the Sun at the center of the Universe with Earth and the planets revolving around the Sun. The stars were a fixed background far away from the Sun.
Copernicus’s theory was not readily accepted by the European society he was addressing. To prove Copernicus wrong, Tycho Brahe (1546–1601) undertook meticulous measurements of the planetary positions relative to the background stars, which are known as “sidereal measurements.” However, one of Brahe’s students, Johannes Kepler (1571–1630), examined this data and became a supporter of the Copernican theory. Kepler used Brahe’s measurements of Mars to prove that Mars had an elliptical orbit around the Sun. By this time it was known that the Martian year was 687 days and that Earth’s year was 365.25 days. Kepler determined that the average time for the Sun, Earth, and Mars to change from a straight-line position to a rightangled triangle was 105.5 days. During this time Earth has moved through
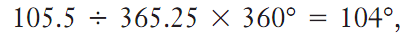
and Mars had moved through only 105.5÷687 x 360° =55°.

Thus the right triangle contained an angle of 104° - 55° = 49°. Because the value of the distance of Earth to the Sun was unknown, Kepler defined this measurement to be 1 astronomical unit (1 AU). Using trigonometric ratios in the right triangle proved that the orbit of Mars was 1.524 AU.
The Significance of Determining Earth’s Circumference.
In 1617, the Dutch scientist Willebrord Snell completed a new assessment of the circumference of Earth and calculated it to be 24,024 miles. With an accurate value for the circumference of Earth, it was consequently possible to determine the distances between places on the different continents. Long baselines were now available to measure the distances to the planets, but there was also a need for accurate instruments for measuring angles. By 1672, the French Academy had telescopes whose scales were able to measure just a few seconds of arc (a second is 1 /3600 th of a degree and 1/1,2916,000part of a circle). An expedition was sent to Cayenne in French Guyana to measure the position of Mars at the same time the measurement was also made in Paris.
Using these measurements, the distance of Mars from Earth was calculated.
More importantly, the use of Kepler’s planetary laws enabled astronomers to find the distance from each of the then known planets to the Sun, as well as the radius of Earth’s orbit.
Once the radius of Earth’s orbit was known, it was possible to relate the Astronomical Unit to our everyday units of measure. Kepler had shown that planets do not rotate about the Sun in circles, but trace out ellipses. The Astronomical Unit is now defined as the length of the semi-major axis of Earth to the Sun, or 149,597,892 km (kilometers).
Using Parallax to Measure Distances
Although there is a limit to the baseline that can be used on Earth, a journey into space is not needed to get longer baselines. If observations of distant objects are made six months apart, the diameter of Earth’s orbit can be used as the baseline. Because the French had calculated the radius of Earth’s orbit, the diameter was also known. However, another problem arises: How do you measure the angles to a distant star or planet with re- spect to Earth’s diameter? This problem is overcome by using a concept known as parallax.
To understand parallax, hold up a finger with one arm fully extended and one eye closed. Look at your finger and also the distant background; now swap the eye that is closed. You should notice that your finger appears to move against the distant background. This is the idea behind parallax measurements.
By carefully observing the stars, it can be noted that although some are very distant, they appear to maintain the same relative position to each other; this is the distant background. In contrast, stars that appear closer to us seem to move during the year relative to the background stars.
Using the figure below, the angle between the star of interest and a reference star may be observed. This is the angle SE1R1. Exactly six months later, the angle between the reference star and the star of interest forms the angle SE2R2. Because the reference star is so distant, the lines E1R1 and E2R2 can be considered to be parallel. Therefore angle E1XE2 = angle SE2R2, and the angle E1SE2 (∠3 +∠1 = ∠2) may be calculated. This angle is known as the parallax of a star. The measurement that astronomers use is called the “stellar parallax” and is half the angle E1SE2.
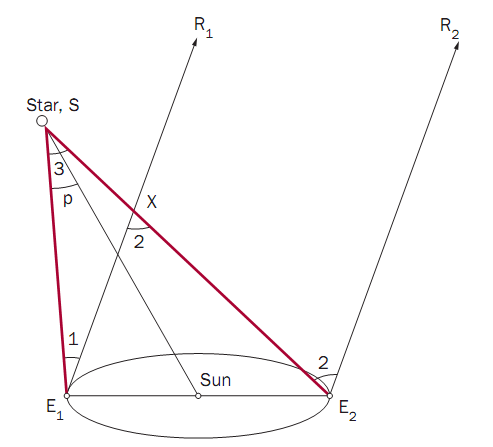
Because the angles involved in parallax measurements are very small their radian measurement can be used to determine the distance of the star from the Sun using the formula:
Distance from the Sun to a star= 1/p AU.
Light Years and Parsecs
The large numbers involved with the nearest distances of stars prompted astronomers to find alternative units of measure. Two such units are used:
the light year and the parsec. The “light year” is the distance a photon of light would travel in vacuum in one year, and is a distance of 9.46 1012 km, or 63,200 AU. The “parsec” was first described in 1913 and is the distance that corresponds with a parallax of one second of arc. The parsec is a distance of 206,265 AU, which is 3.26 light years or 3.086 1013 km.
Modern instruments on Earth can measure a parallax of up to one hundredth of a second—anything smaller than this is affected by Earth’s atmosphere. This restricts our measurement of astronomical distances on Earth to 100 parsecs. There are only 5,000 stars out of the millions visible that are within the 100 parsec range. In 1989, the European Space Agency launched the satellite Hipparcos, which could measure angles of one thousandth of a second, a distance of 1000 parsecs. Hipparcos allowed astronomers to accurately measure the distance of many more thousands of stars.
Measuring the Brightness of Stars
Around 129 B.C.E. Hipparchus introduced a scale of brightness to help distinguish one star from another. By his scale, a star of a magnitude of 6 is the faintest star the unaided eye can see, and stars that are 100 times as bright or greater have a magnitude of 1. In the early twenty-first century, scientific instruments are available that can measure the brightness of stars with a precision undreamed of by Hipparchus, who only had a personal
judgment to determine relative brightness.
In 1856, Norman Pogson proposed that the difference of 5—the difference between stars of a magnitude of 1 and 6—be set at exactly 100 times magnitude. The difference in brightness between stars that differ by one magnitude of brightness is thus 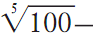 that is, one is 2.152 brighter than the other. The ability to accurately measure the intensity of a star is important because a star’s brightness drops off inversely to the square of the distance from a star. The brightness of a star is also dependent on its temperature, and the temperature will have an effect on the spectrum the star emits. If two stars with identical spectra are observed, and the distance of one of the stars through parallax measurement is known, their brightness can be compared. The variance in brightness is attributable to the difference in distance. Using the inverse square law, the distance of the star whose distance was previously unknown can be determined.
that is, one is 2.152 brighter than the other. The ability to accurately measure the intensity of a star is important because a star’s brightness drops off inversely to the square of the distance from a star. The brightness of a star is also dependent on its temperature, and the temperature will have an effect on the spectrum the star emits. If two stars with identical spectra are observed, and the distance of one of the stars through parallax measurement is known, their brightness can be compared. The variance in brightness is attributable to the difference in distance. Using the inverse square law, the distance of the star whose distance was previously unknown can be determined.
Stars can give off radiation not only in the visible spectrum but also as radio waves, x-rays, and gamma rays. All of these different parts of the elec- tromagnetic spectrum can be used in conjunction with the techniques already discussed to make astronomical measurements.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Reference
Heath, Sir Thomas. Aristarchus of Samos, the Ancient Copernicus. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1913.
Leverington, David. A History of Astronomy from 1890 to the Present. London: Springer-Verlag, 1995.
Van Zyl, J. E. Unveiling the Universe. London: Springer-Verlag, 1996.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|