
Vowels PRICE, PRIZE
 المؤلف:
Erik R. Thomas
المؤلف:
Erik R. Thomas
 المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
 الجزء والصفحة:
311-17
الجزء والصفحة:
311-17
 2024-03-22
2024-03-22
 1357
1357
Vowels PRICE, PRIZE
Monophthongization of PRICE (i.e., /ai/ before voiceless consonants) and, especially, PRIZE (i.e., other phonetic contexts of /ai/) is stereotypically associated with the American South. However, glide weakening is a more accurate term because it encompasses both monophthongal forms and variants with a glide that is only partly truncated, both of which are perceived as “flattened” by outsiders. Both forms are common and widespread.
Glide weakening has, since the late 19th century, occurred throughout the South except for a few Atlantic coastal areas, and even there it has shown signs of encroaching recently. Where weakening occurs, it consistently affects contexts before liquids most strongly and those before voiceless consonants least strongly, but the relative strength of the effects of following pauses, nasals, and voiced obstruents is a matter of dispute. Weakening produces forms such as [a:ε~a:æ], leading ultimately to monophthongal [a:]. Some speakers show forms such as [æ:] and  , but [a:] is more usual.
, but [a:] is more usual.
Weakening before voiceless consonants (PRICE) is geographically and socially restricted. It is found mainly in Appalachia (south to northern Alabama), Arkansas, Oklahoma, Texas, the Piney Woods Belt, and parts of the North Carolina coastal plain, but some working class speakers elsewhere show it. It has long been associated with working-class speech, and hence many upper-middle class speakers avoid it. Weakening in any context (PRICE or PRIZE) is apparently declining around the margins of the South, such as in Maryland and Oklahoma. Speakers with aspirations of upward white-collar mobility often avoid it, though such avoidance is not as prevalent in rural areas as in urban areas.
Glide weakening was traditionally absent on the eastern shore of the Chesapeake Bay, around the Pamlico Sound, and in the Low Country of South Carolina and Georgia. In the former two areas, backing of the nucleus occurred instead in all contexts. Forms such as [a:e] were usual, with 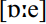 and
and  occurring sporadically. Backing occurred for PRIZE in the Low Country. Such backing also occurs widely in the South before voiceless consonants (PRICE) where that context remains diphthongal. Another variation reported from older speech in Tidewater and Piedmont Virginia and the South Carolina/Georgia Low Country for contexts before voiceless consonants is
occurring sporadically. Backing occurred for PRIZE in the Low Country. Such backing also occurs widely in the South before voiceless consonants (PRICE) where that context remains diphthongal. Another variation reported from older speech in Tidewater and Piedmont Virginia and the South Carolina/Georgia Low Country for contexts before voiceless consonants is 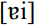 , with a higher nucleus. Acoustic analyses indicate that only some speakers from those areas showed
, with a higher nucleus. Acoustic analyses indicate that only some speakers from those areas showed 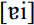 .
.
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


