


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 22-11-2020
Date: 24-7-2020
Date: 6-2-2017
|
Measuring distance in the Solar System: The planets
It will be shown later that it is relatively easy to obtain accurately the distances of the planets from the Sun in units of the Earth’s distance from the Sun. If, therefore, the distance of any planet from the Earth can be accurately measured in kilometres at any time, all the planetary heliocentric distances can be found in kilometres. In particular, the astronomical unit (the mean distance of the Earth from the Sun) can be obtained in kilometres.
All the classical parallax methods are hopelessly inaccurate where the distance of a planetary body is concerned. The Moon’s distance is about thirty times the Earth’s diameter, which is essentially the length of the available base-line. The distance of the asteroid Eros, at its closest approach, however, is some 20 000 000 km, or about 1500 times the length of the base-line. Shows that it is not possible to obtain the geocentric parallax of Eros to high accuracy by this method.
Some improvement in accuracy is obtained by using one observatory, instead of two. In this way, the factors of different instrument errors and weather conditions, which control refraction, can be avoided. The base-line is provided by taking observations of the asteroid at different times so that in the time interval involved, the observatory moves due to the Earth’s diurnal movement and orbital motion. The observing programme is carried out around the time of opposition when the planet is
near the observer’s meridian at midnight. Observations are made a few hours before midnight and a few hours after midnight. Before the development of radar, many observatories carried out such observing programmes, notably between 1900 and 1901 and between 1930 and 1931, when Eros was in opposition. The value of the solar parallax derived from these programmes was probably not any more accurate than one part in a thousand.
Nowadays, the use of powerful radio telescopes as radar telescopes has enabled the accuracy to be increased by a factor of at least one hundred. The geocentric distance of the planet Venus has been measured repeatedly by this method. It consists essentially of timing the interval between transmission of a radar pulse and the reception of its echo fromVenus. This interval, with a knowledge of the velocity of electromagnetic radiation (the speed of light) enables the Earth–Venus distance to be found. Thus, if EV, c and t are the Earth–Venus distance, velocity of radio waves and time interval respectively,
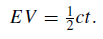
Various corrections have to be made to derive the distance Venus-centre to Earth-centre. For example, the distance actually measured is the distance from the telescope to the surface of Venus. The effect of the change of speed of the radar pulse when passing through the ionosphere also has to be taken into account.
An even more accurate value of the solar parallax has been obtained by tracking Martian artificial satellites such as Mariner 9 over extended periods of time. Range and range rate measurements (i.e. line of sight distance and speed by radio tracking) allow the distance Earth-centre to Mars-centre to be found.



|
|
|
|
"إنقاص الوزن".. مشروب تقليدي قد يتفوق على حقن "أوزيمبيك"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين تحقق اختراقا بطائرة مسيرة مزودة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تطلق النسخة الحادية عشرة من مسابقة الجود العالمية للقصيدة العمودية
|
|
|