


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 26-5-2016
Date: 24-2-2016
Date: 12-7-2020
|
Atmospheric refraction: Measurement of the constant of refraction
The constant of refraction, k, may be measured by using the transits of a circumpolar star. It has been seen that the effect of refraction is to displace the star towards the zenith along the vertical through star and zenith. Thus, in figure 1, an observer in latitude φ notes that a star has upper and lower culminations at A and B respectively. Let the observed zenith distances of A and B be ζA and ζB respectively. In the absence of refraction, the upper and lower transits would have been seen to be at positions C and D on the celestial sphere, where PC = PD = 90 − δ, δ being the star’s declination.
Note: if the declination of the star was such that the upper transit had been north of the zenith, the observed path of the star would have intersected the parallel of declination it would have followed in the absence of refraction.
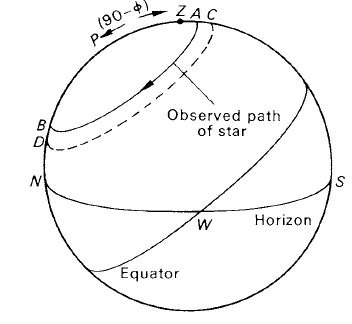
Figure 1. Measurement of an angle of refraction.
R = k tan ζ........(1)
Now by equation (1),
CA = k tan ζA DB = k tan ζB
so that we have
ZC = ζA + k tan ζA ZD = ζB + k tan ζB.
But
ZC = PC − PZ = 90 − δ − (90 − ∅) = ∅ − δ.
Hence,
∅ − δ = ζA + k tan ζA.......... (2)
Similarly,
ZD = ZP + PD = 90 − ∅ + 90 − δ = 180 − ∅ − δ
so that
180 − ∅ − δ = ζB + k tan ζB.......... (3)
If the observer’s latitude were accurately known, the two equations (2) and (3) in the two unknowns δ and k could be solved to yield values of δ and k. But because of small changes in the Earth’s crust, small variations take place in the latitude of the telescope used. In practice, therefore, at least two circumpolar stars are observed, within a short period of time, so that two more equations are obtained, namely
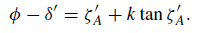 ........(4)
........(4)
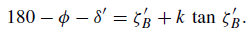 ...........(5)
...........(5)
The four equations (2)–(5) are now solved to give values of δ, δ', ∅ and k.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|