


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 23-12-2019
Date: 18-12-2019
Date: 21-12-2019
|
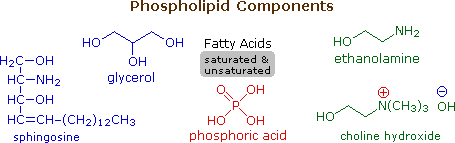
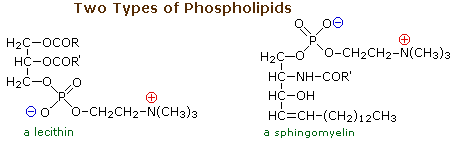
Phospholipids are the main constituents of cell membranes. They resemble the triglycerides in being ester or amide derivatives of glycerol or sphingosine with fatty acids and phosphoric acid. The phosphate moiety of the resulting phosphatidic acid is further esterified with ethanolamine, choline or serine in the phospholipid itself. The following diagram shows the structures of some of these components.
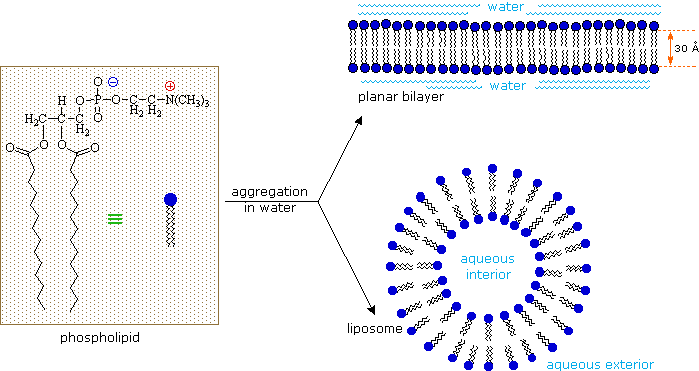
As ionic amphiphiles, phospholipids aggregate or self-assemble when mixed with water, but in a different manner than the soaps and detergents. Because of the two pendant alkyl chains present in phospholipids and the unusual mixed charges in their head groups, micelle formation is unfavorable relative to a bilayer structure. If a phospholipid is smeared over a small hole in a thin piece of plastic immersed in water, a stable planar bilayer of phospholipid molecules is created at the hole. As shown in the following diagram, the polar head groups on the faces of the bilayer contact water, and the hydrophobic alkyl chains form a nonpolar interior. The phospholipid molecules can move about in their half the bilayer, but there is a significant energy barrier preventing migration to the other side of the bilayer.
This bilayer membrane structure is also found in aggregate structures called liposomes. Liposomes are microscopic vesicles consisting of an aqueous core enclosed in one or more phospholipid layers. They are formed when phospholipids are vigorously mixed with water. Unlike micelles, liposomes have both aqueous interiors and exteriors.
A cell may be considered a very complex liposome. The bilayer membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the surrounding fluids is largely composed of phospholipids, but it incorporates many other components, such as cholesterol, that contribute to its structural integrity. Protein channels that permit the transport of various kinds of chemical species in and out of the cell are also important components of cell membranes.
The interior of a cell contains a variety of structures (organelles) that conduct chemical operations vital to the cells existence. Molecules bonded to the surfaces of cells serve to identify specific cells and facilitate interaction with external chemical entities.
The sphingomyelins are also membrane lipids. They are the major component of the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers. Multiple Sclerosis is a devastating disease in which the myelin sheath is lost, causing eventual paralysis.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|