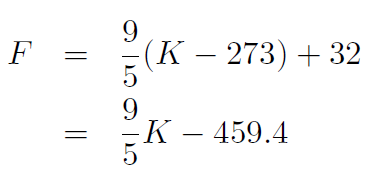تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Celsius, Farenheit and Kelvin Temperature Scales
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
الجزء والصفحة:
p 212
30-12-2016
1645
Celsius, Farenheit and Kelvin Temperature Scales
The antiquated Farenheit temperature scale is only still used in a few countries (including the United States). Water freezes at 32oF and boils at 212oF. A much more natural temperature scale, called Celsius or Centigrade, rates the freezing and boiling point of water at 0oC and 100oC respectively. To convert between the two scales use
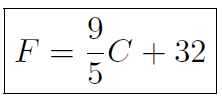
where F is the temperature in Farenheit and C is the temperature in Centigrade.
Example If you set your house thermo state to 70oF what is the temperature in Centigrade ?
Solution
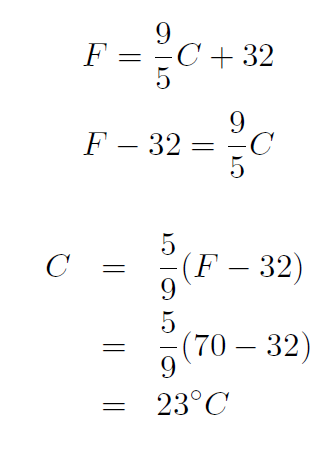
Example At what temperature are the Farenheit and Centigrade scales equal ?
Solution When they are equal the F = C = x giving
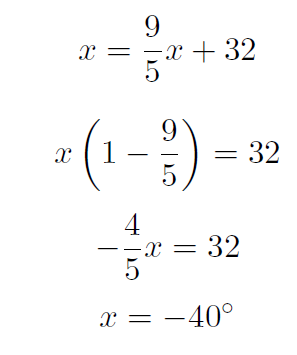
i.e.
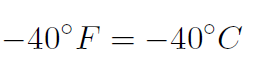
The temperature of a substance is related to the speed of the individual molecules which also give rise to pressure. Thus a gas which has fast moving molecules will have a high temperature and pressure. What happens if we slow all the molecules to zero speed? Well then the gas pressure will be zero. The temperature at which this happens is -273:15oC. This leads to a third type of tmperature scale called Absolute temperature or Kelvin temperature. The Kelvin temperature at which a gas has zero pressure is defined to be 0oK. Thus
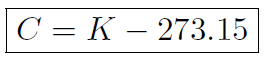
where C is the temperature in Centigrade and K is the temperature in Kelvin.
Example What is the relationship between Farenheit and Kelvin?
Solution
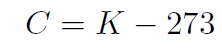
and
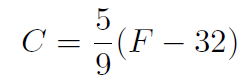
giving
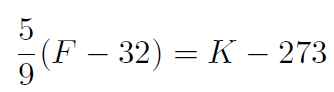
or