
Nucleus
 المؤلف:
T. Sargunam Stephen
المؤلف:
T. Sargunam Stephen
 المصدر:
Biology (Zoology)
المصدر:
Biology (Zoology)
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:

 2514
2514
Nucleus
The nucleus is the most important organelle of cell. It controls all metabolic processes and hereditary activities of the cell.
The nucleus was first discovered and named by Robert Brown in 1833. The occurrence of a nuclear membrane was first revealed by O. Hertwig in 1893. The nucleus is found in all the eukaryotic cells of plants and animals.
However some eukaryotic cells such as the sieve tubes of higher plants and mammalian erythrocytes have no nucleus. Usually the cells contain single nucleus (mononucleate). However certain cells may have more than one nuclei. Accordingly they may be called binucleate or polynucleate cells. The polynucleate cells of the animals are called syncytial cells (Osteoblast cells)
The shape of the nucleus may be spherical, elliptical or discoidal. In certain cells the nucleus is irregular in shape.
The size of the nucleus may vary from 3 µm to 25 µm in diameter. The size is directly proportional to that of the cytoplasm. Nuclear size may also be determined by the number of chromosomes or ploidy. The nucleus of the haploid cells are smaller than that of the diploid cells.
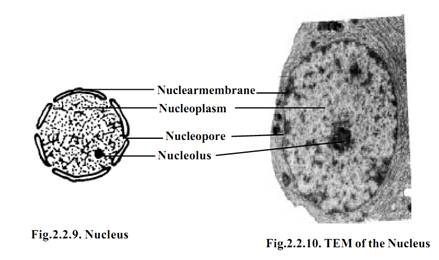
The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope. This envelope is comprised of two membranes of 5-10 nm thickness. The inner nuclear membrane supports a fibrous sheath called the nuclear lamina. The inner nuclear membrane is surrounded by the outer nuclear membrane. The space between the inner and outer membranes is known as perinuclear space. It is a 10 to 50 nm wide fluid filled compartment.
The nuclear lamina is a protein meshwork. It is a very dynamic structure. The nuclear envelope is perforated by nuclear pores. Each pore has a diameter between 10 nm to 100 nm. It has been calculated that the nuclear pores account for 5 to 15 percent of the surface area of the nuclear membrane. There is continuous movement of molecules across the nuclear envelope through the pores.
The nucleus is filled with a transparent semisolid matrix known as nucleoplasm or nuclear sap. The chromatin threads and the nucleolus remain suspendended in the nucleoplasm. The nucleoplasm is composed of nucleoproteins, proteins, enzymes and minerals.
The nucleoplasm contains several thread like coiled structures. These are the chromatin fibres. During the cell division they become thick ribbon like structures known as chromosomes. The chromatin is made up of Deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) and proteins.
The nucleus contains one or more spherical colloidal structures called nucleoli. The size of nucleolus is related to the synthetic activity of the cell. The number of nucleoli in the cells may be one, two or four. Chemically, nucleolus contains DNA of nucleolar origin, four types rRNA, 70 types of ribosomal proteins, RNA binding proteins and RNA splicting nucleoproteins.
Ribosomal subunits are synthesized in the nucleolus. Initiation, production and maturation stages of ribosomal formation happen in three distinct regions of the nucleolus.
Chromosomes
The chromatin fibres get condensed into chromosomes during cell divisions. They are capable of self-reproduction and they play an important role in heredity.
The nucleus was first observed and described by karl Nagli (1842) in the nuclei of plant cells. Chromosomes and their role in cell division were first explained by A. Schneider (1873). In 1887 Benden and Bovery reported that the number of chromosomes for each species is constant. T. H Morgan and H. Muller in 1922 revealed the occurrence of nearly 2000 genetic factors on four chromosomes of Drosophila. In 1924, Robert Feulgen showed that chromosomes contain DNA.
The number of chromosomes is constant for a particular species. The reproductive cells such as sperm or ovum has one set of chromosomes and it is known as the haploid set (n). It is also known as the genome. The somatic or body cells contain two haploid set or genomes and are known as the diploid cells (2n). The diploid condition is arrived at by the union of the haploid male and female gametes in the sexual reproduction.
Number of Chromosomes
Common name Scientific name Chromosome Number
Paramoecium P. aurelia 30-40
Hydra H. vulgaris 32
Housefly Musca domestica 12
Fruit fly Drosophila sps 8
Pigeon Columba livia 80
Gorilla Gorilla gorilla 48
Man Homo sapiens 46
The size of a chromosome can be measured during mitotic metaphase. It may range from 0.25 µm to 30 µm.
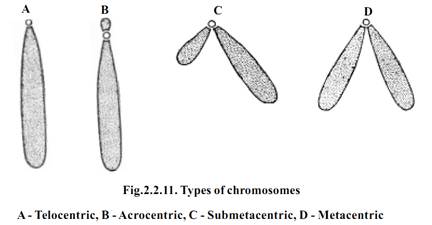
The shape of the chromosome changes from phase to phase. Each chromosome has a clear zone, known as centromere or kinetocore along their length. The centromere divides the chromosome into two parts. Each part is called the chromosome arm. Thus according to the position of the centromere and nature of the chromosome arm, the chromosomes may be Telocentric, Acrocentric, Submetacentric and Metacentric.
References
T. Sargunam Stephen, Biology (Zoology). First Edition – 2005, Government of Tamilnadu.
 الاكثر قراءة في البايلوجيا الخلوية
الاكثر قراءة في البايلوجيا الخلوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


