
Mitochondria
 المؤلف:
T. Sargunam Stephen
المؤلف:
T. Sargunam Stephen
 المصدر:
Biology (Zoology)
المصدر:
Biology (Zoology)
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 4-11-2015
4-11-2015
 2315
2315
Mitochondria
The mitochondria are filamentous or granular cytoplasmic organelles of all aerobic cells of higher animals and plants. They are also found in microorganisms including Algae, Protozoa and Fungi.
They were first observed by Kolliker in 1850 as granular structures in the striated muscles. The name ‘mitochondria’ was given to them by Benda (1897-98). Various steps of glycolysis in mitochondria were discovered by two German biochemists Embden and Meyerhof. Embden got the Nobel Prize in 1922. Sir Hans Adolph Krebs, in 1937 found out various reactions of citric acid cycle. Kennedy and Lehninger (1948-50) showed that Citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid oxidation took place in the mitochondria.
The number of mitochondria in a cell depends on the type and functional state of the cell. Certain cells contain large number of mitochondria e.g., eggs of sea urchin contain 140,000-150,000 mitochondria. Oocytes of amphibians contain 300,000 mitochondria. Liver cells of rat contain only 500¬1600 mitochondria. Some algal cells may contain only one mitochondrion.
The mitochondria may be filamentous or granular in shape. They vary in size from 0.5 µm to 2.0 µm. Due to their minute nature they cannot be seen under light microscope.
Each mitochondrion is bound by two highly specialized membranes. The outer membrane is smooth. It is separated from the inner membrane by a 6-8 nm wide space. The inner membrane is highly convoluted, forming a series of inflodings known as cristae.
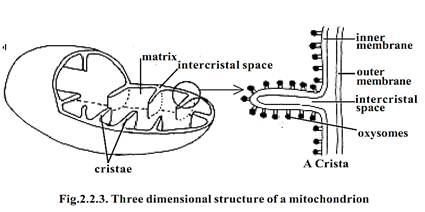
Thus mitochondria are double membrane envelopes. The inner membrane divides the mitochondrial space into two distinct chambers. The outer compartment is the peri-mitochondrial space. It is found between outer and inner membranes. The inner compartment is the matrix space. It is filled with a dense gel like substance called mitochondrial matrix. The matrix contains lipids, proteins and circular DNA molecules.
The outer and inner membranes, intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix contain several enzymes. Hence the mitochondria perform several important functions such as oxidation, dehydrogenation, oxidative phosphorylation and respiratory chain of the cell.
Since mitochondria play a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates and fats, they are considered as the actual respiratory organs of the cells. During such biological oxidations large amount of energy is released. The energy is utilized by the mitochondria for synthesis of the energy rich compound known as adenosine tri phosphate or ATP. Due to this function, the mitochondria are also known as “power houses” of the cell. In animal cells mitochondria produce 95 % of ATP molecules.
References
T. Sargunam Stephen, Biology (Zoology). First Edition – 2005, Government of Tamilnadu.
 الاكثر قراءة في البايلوجيا الخلوية
الاكثر قراءة في البايلوجيا الخلوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


