
Mandarin Chinese (Sino-Tibetan)
 المؤلف:
Rochelle Lieber
المؤلف:
Rochelle Lieber
 المصدر:
Introducing Morphology
المصدر:
Introducing Morphology
 الجزء والصفحة:
122-7
الجزء والصفحة:
122-7
 22-1-2022
22-1-2022
 2335
2335
Mandarin Chinese (Sino-Tibetan)
Where the genius of Turkish morphology lies in the exuberance of its processes of suffixation, Mandarin Chinese makes entirely different choices from our universal toolkit, although it too concentrates on just a few tools.
According to Li and Thompson (1971), Mandarin has no processes of prefixation to speak of, and it has only a tiny handful of suffixes, among them the three in (11):2
The suffix -xué attaches to nouns to make nouns meaning ‘the study of X’, and -jiā makes personal nouns, also from other nouns. Notice that in the example kēxué-jiā, both suffixes occur. The third suffix -huà makes verbs from nouns and adjectives. Suffixation is quite limited in Mandarin though: there are relatively few suffixes, and we certainly do not find words of the complexity of those in Turkish or even of words in English. Mandarin also has full reduplication, which it uses for two purposes. Verbs can be reduplicated to form derived verbs meaning ‘X a little’:

And some adjectives can be reduplicated to make intensive adjectives, that is, adjectives that mean ‘very X’:

Though Mandarin is relatively poor in affixation and reduplication, it is incredibly rich in compounding. Mandarin has not only compound nouns and compound adjectives, as English does, but also all sorts of com�pound verbs, as the examples in (14) show:

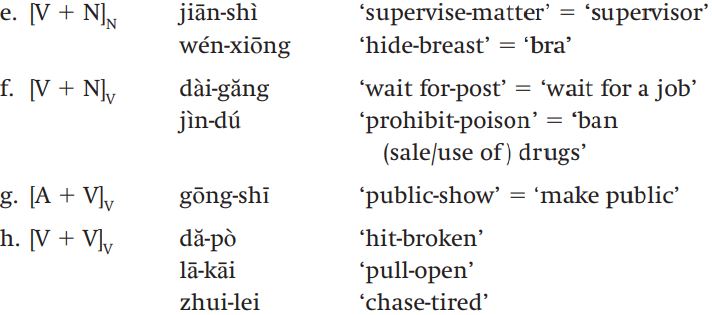
As the examples in (14) show, Mandarin has many different types of com�pound, indeed, many more types than English, which as we’ve seen has very productive compounding processes. In Mandarin, some compounds are attributive, for example those in (14a) and (14d). The examples in (14b, c) are coordinative compounds. And some are subordinative, for example those in (14e, f, g). Most of these compounds are endocentric (14a, b, c, d, f, g, h), but those in (14e) are exocentric. Some are right-headed (14a, c, d, f, g), some have two heads (the coordinate compounds in (14b, c)), and some are left-headed (14h).
The examples we have given above all concern lexeme formation in Mandarin because Mandarin has rather little in the way of inflection. Nouns are not inflected for number, nor do verbs inflect for person or number. Tense is not marked morphologically and aspect is marked only by separate particles that appear after the verb. Mandarin does have a system of noun classifiers that are used when counting or otherwise quan�tifying nouns, but again separate particles rather than affixes are used to mark the class of particular nouns. So we can return to the sentences we looked at, and see them in the wider context of Mandarin morphology:

The verb jian ‘see’ doesn’t change its form from one aspect to another, nor does the noun chang jing lu ‘giraffe’ change from singular to plural. In order to signal more than one giraffe, one needs to signify a specific number or quantity.
What this shows us is that Mandarin is just as able as Turkish to come up with new words and to express grammatical distinctions, but its strategy for doing so makes use of different means.
 الاكثر قراءة في Morphology
الاكثر قراءة في Morphology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


