

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Peptides Can Be Distinguished by Their Ionization Behavior
المؤلف:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
المصدر:
Book or Source : Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th ed 2012
الجزء والصفحة:
p 86
11-4-2017
3833
Peptides Can Be Distinguished by Their Ionization Behavior
Peptides contain only one free α-amino group and one free α-carboxyl group, at opposite ends of the chain (Fig. 1.1). These groups ionize as they do in free amino acids, although the ionization constants are different because an oppositely charged group is no longer linked to the α carbon. The α-amino and α-carboxyl groups of all nonterminal amino acids are covalently joined in the peptide bonds, which do not ionize and thus do not contribute to the total acid-base behavior of peptides.
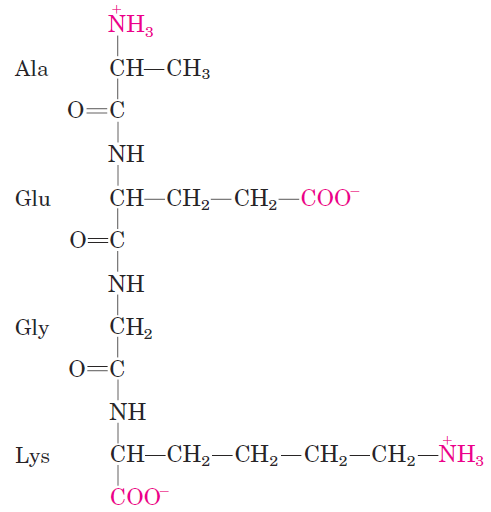
FIGURE 1.1 Alanylglutamylglycyllysine. This tetrapeptide has one free α-amino group, one free α-carboxyl group, and two ionizable R groups. The groups ionized at pH 7.0 are in red.
However, the R groups of some amino acids can ionize and in a peptide these contribute to the overall acid-base properties of the molecule (Fig. 1.1). Thus the acid-base behavior of a peptide can be predicted from its free α-amino and α-carboxyl groups as well as the nature and number of its ionizable R groups. Like free amino acids, peptides have characteristic titration curves and a characteristic isoelectric pH (pI) at which they do not move in an electric field. These properties are exploited in some of the techniques used to separate peptides and proteins, as we shall see later in the chapter. It should be emphasized that the pKa value for an ionizable R group can change somewhat when an amino acid becomes a residue in a peptide. The loss of charge in the α-carboxyl and α-amino groups, the interactions with other peptide R groups, and other environmental factors can affect the pKa. s.
 الاكثر قراءة في الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات
الاكثر قراءة في الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















