
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
The gravitational telescope in the Galactic Center
المؤلف:
Heino Falcke and Friedrich W Hehl
المصدر:
THE GALACTIC BLACK HOLE Lectures on General Relativity and Astrophysics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 261
6-2-2017
2028
The gravitational telescope in the Galactic Center
The MBH in the Galactic Center is a telescope with a lens of effective diameter ∼4 × 1017 cm (for a source at infinity) and a focal length of ∼2.5 × 1022 cm. Unfortunately, Nature did not design it as an ideal telescope. A point mass lens does not produce faithful images of the lensed sources, the optical axis is heavily obscured by interstellar dust, and the telescope points in a fixed direction, which is not of our choosing. In fact, various estimates suggest that there are not enough luminous sources in that direction for gravitational lensing to be important for present day observations, although future, deep observations may pick up lensing events (Wardle and Yusef-Zadeh 1992, Alexander and Sternberg 1999, Alexander and Loeb 2001). Nevertheless, it is worthwhile to consider the possible roles of gravitational lensing in the observations and the study of the Galactic Center. This is important not only in anticipation of future observations, but also because the estimates of the lensing probability are quite uncertain (they involve models of
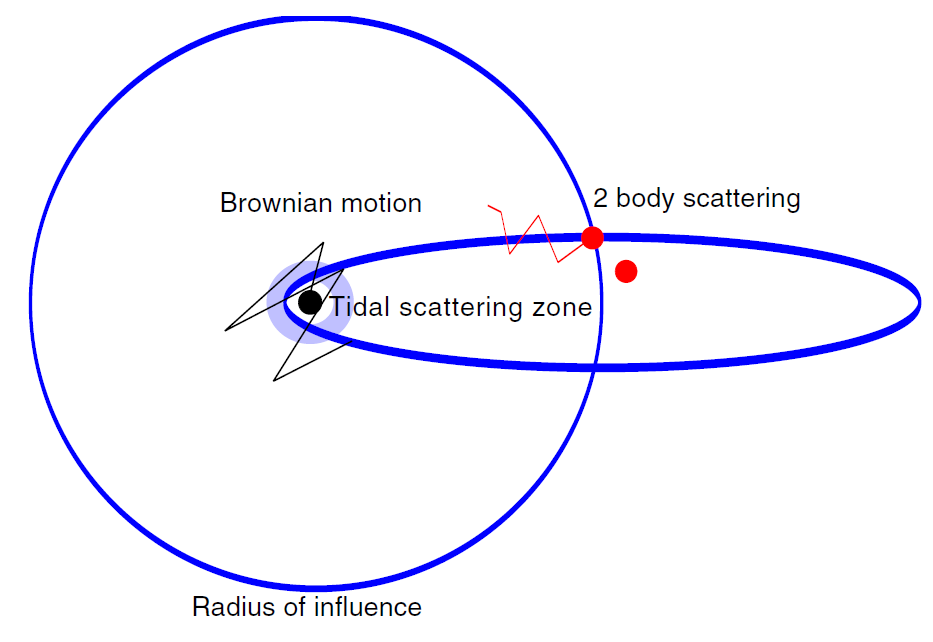
Figure 1.1. A schematic representation of the tidal scattering process. A star initially orbiting the MBH at the radius of influence is scattered by a two-body encounter into an extremely eccentric orbit that brings it to the tidal scattering zone just outside the tidal disruption radius. The star suffers an extreme, non-disruptive tidal interaction with the MBH, and continues on its way out of the radius of influence, where it is scattered by frequent two-body encounters. In the meanwhile, the Brownian motion of the MBH due to its interactions with the stellar system causes it to move away from its original position. Both these random processes significantly increase the chances of the tidally disturbed star surviving total disruption during subsequent orbits.
the unobserved far side of the Galaxy), and because there are hints that lensing may not be quite as rare as predicted.
Gravitational lensing may be used to probe the dark mass (is it really a MBH?) and the stars around it, and to locate the MBH on the IR grid, where the stars are observed. However, gravitational lensing can also complicate the interpretation of the observations since it affects many of the observed properties of the sources: flux, variability, apparent motion and surface density. IR flares due to lensing can be confused with those due to fluctuations in the accretion flow, and lensed images of background sources far behind the MBH can be confused with stars that are truly near the MBH. This section will focus on aspects of gravitational lensing that are or may be relevant for the Galactic Center.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















