
Organisms Transform Energy and Matter from Their Surroundings
 المؤلف:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
المؤلف:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
 المصدر:
Book or Source : Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th ed 2012
المصدر:
Book or Source : Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th ed 2012
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 22
الجزء والصفحة:
p 22
 11-9-2016
11-9-2016
 2631
2631
Organisms Transform Energy and Matter from Their Surroundings
For chemical reactions occurring in solution, we can define a system as all the reactants and products present, the solvent that contains them, and the immediate atmosphere—in short, everything within a defined region of space. The system and its surroundings together constitute the universe. If the system exchanges neither matter nor energy with its surroundings, it is said to be isolated. If the system exchanges energy but not matter with its surroundings, it is a closed system; if it exchanges both energy and matter with its surroundings, it is an open system. A living organism is an open system; it exchanges both matter and energy with its surroundings. Living organisms derive energy from their surroundings in two ways: (1) they take up chemical fuels (such as glucose) from the environment and extract energy by oxidizing them or (2) they absorb energy from sunlight. The first law of thermodynamics, developed from physics and chemistry but fully valid for biological systems as well, describes the principle of the conservation of energy: in any physical or chemical change, the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant, although the form of the energy may change. Cells are consummate transducers of energy, capable of interconverting chemical, electromagnetic, mechanical, and osmotic energy with great efficiency (Fig. 1–1).
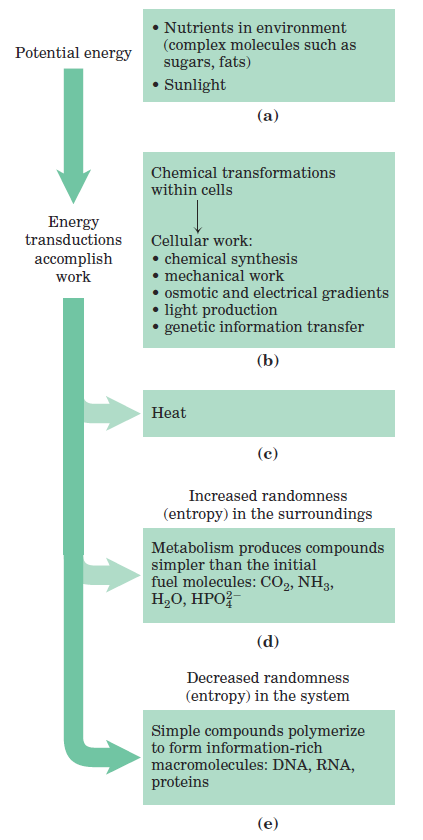
FIGURE 1–1 Some energy interconversion in living organisms. During metabolic energy transductions, the randomness of the system plus surroundings (expressed quantitatively as entropy) increases as the potential energy of complex nutrient molecules decreases. (a) Living organisms extract energy from their surroundings; (b) convert some of it into useful forms of energy to produce work; (c) return some energy to the surroundings as heat; and (d) release end-product molecules that are less well organized than the starting fuel, increasing the entropy of the universe. One effect of all these transformations is (e) increased order (decreased randomness) in the system in the form of complex macromolecules.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


