

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Atom Hybridization and Acid/Base Strength
المؤلف:
ADAM RENSLO
المصدر:
the organic chemistry of medicinal agent
الجزء والصفحة:
p259
12-7-2016
3006
Atom Hybridization and Acid/Base Strength
Acidic X–H bonds are always covalent single bonds (σ bonds) arising from overlap of an atomic orbital on the X atom and the 1s orbital of H. The most common X atoms in organic molecules will be C, N, or O atoms involved in single, double or triple bonds. The σ-bonding orbitals associated with individual C, N, and O atoms are frequently envisioned as hybrid orbitals with varying degrees of s and p character, depending on the type of hybridization (sp, sp2, or sp3). Experimentally, it is observed that as hybridization of the orbital involved in an X–H bond changes from sp3 → sp2 → sp, the X–H bond becomes more acidic. This effect is shown for a series of similar molecules with acidic N–H and O–H bonds in the table (Table 1.1).
Table 1.1 Effect of X Atom Hybridization on Acidities of C–H, N–H, and O–H Acids (R = Methyl).
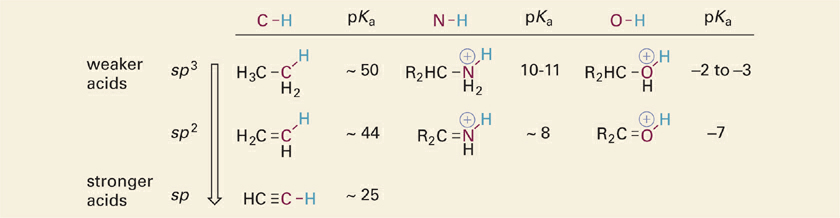
The explanation for this trend is that as the hybridization of an atom changes from sp3 → sp2 → sp, the percentage of “s” character increases from 25% to 33% to 50%. Recall that s orbitals are spherical in shape such that the electrons surround and overlap with the positively charged nucleus. In contrast, p orbitals have a bilobed “dumbbell” shape with a node at the nucleus such that the electrons are distributed further away from the nucleus. Thus, with increasing s character of the bonding orbital on the X atom (C, N, O), electrons in the X–H σ bond interact more strongly with the positively charged nucleus of X and less so with the bound proton. This results in a weakening of the X–H bond strength and an increased acidity (lower pKa).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















