

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Influence of the Surface or Interface on Nanocrystals
المؤلف:
C. Br´ echignac P. Houdy M. Lahmani
المصدر:
Nanomaterials and Nanochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p42
28-2-2016
1753
Influence of the Surface or Interface on Nanocrystals
Changes can thus be observed in the phase diagram of a material by varying only the size of the constituent grains. In the same way, one may expect to obtain similar effects by altering the surface state of these nanograins whilst keeping their dimensions constant. The modification of this surface or interface energy can be achieved in different ways: either by adsorption of various chemical species or molecules in the case of powdered systems or systems in solution (solid–gas or solid–liquid interface), or by compacting the nanograins, or embedding them within a matrix (solid–solid interface).
A Simple Example
Let us return to BaTiO3. Quite recently, the role of the outer interface on transition temperatures in barium titanate has been investigated (Fig. 1).
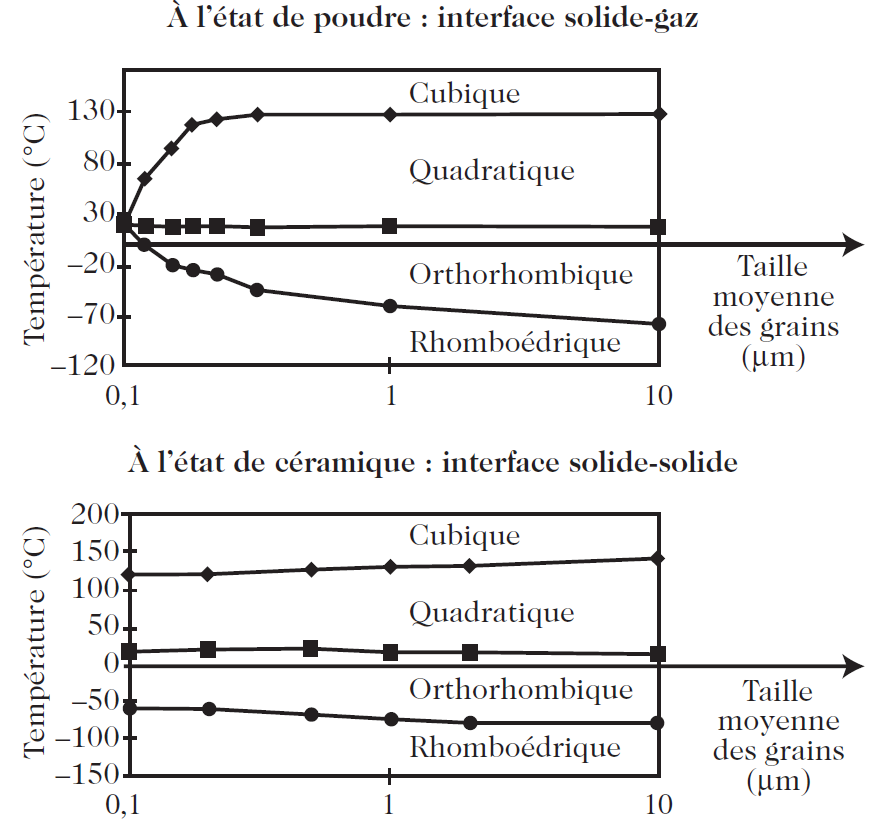
Fig.1. Transition temperatures for BaTiO3 as a function of grain size . Upper: In the powdered state (solid–gas interface). Lower : In the ceramic state (solid–solid interface)
In the first case, BaTiO3 is in powdered form and hence has an outer surface which is a solid–gas interface. In the second case, the material is in the form of a microstructure composed of agglomerated grains, i.e., a ceramic with varying degrees of density. In this case, there is a solid–solid interface between grains. The two phase diagrams are clearly different. Thus, for a given grain size and temperature, different phases can be stabilised depending on the state of the interface.
Still in the second case, for a solid–solid interface, a very slight variation is observed in the transition temperatures as a function of grain size. Nanograins in a bulk solid material would therefore appear to behave like large grains. The surface effect would thus seem to disappear if the nanocrystal is bounded by an outer interface with nanocrystals that are identical to it.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء النانو
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء النانو
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















