

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Adverbs with both sentential and manner function
المؤلف:
R.M.W. Dixon
المصدر:
A Semantic approach to English grammar
الجزء والصفحة:
418-12
2023-04-22
2053
Adverbs with both sentential and manner function
We summarized the properties of adverbs with both sentential and manner function, divided into five sets.
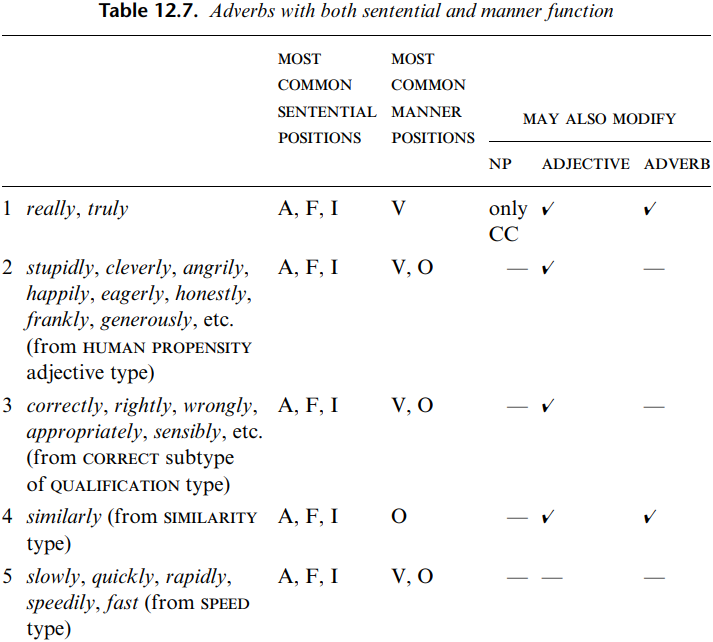
Set (1) involves really and truly, which were in row (h). These are the most omni-functional of adverbs. As illustrated for really, they have all five functions. In addition, they may modify an adverb-plus-adjective, or an adverb-plus-adverb. For example:
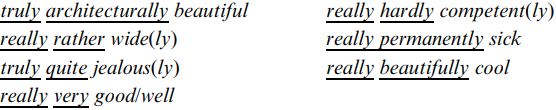
We frequently find these two adverbs coordinated, as one complex adverb; they are always in the order really and truly. For example, He really and truly believed me, and She is really and truly the most beautiful person I have ever seen.
Really and truly often modify an adverb from set (2), which may be repeated. Really or truly may then also be repeated. That is, one can say any of:
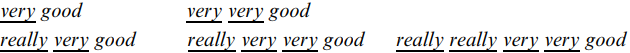
However, really (or truly) is not likely to be repeated unless the following adverb is; that is one would not expect to hear *really really very good. For very could be substituted terribly, awfully, etc.
All of the remaining sets involve adverbs derived from adjectives by the addition of -ly. The way in which stupidly occurs in sentential function at positions A, I and F and in manner function at positions V and O was already illustrated. Using stupidly in sentential function, as in (13a–c), implies that the soldier was stupid to answer the officer’s question, whereas using the adverb in manner function, as in (14a– b), implies that he answered the question in a stupid manner.
Set (2) covers adverbs derived from HUMAN PROPENSITY adjectives. Alongside stupidly we have cleverly, angrily, happily, eagerly and many others. In some contexts it is not easy to identify the different meanings these adverbs have in their sentential and manner functions. However, there always is an implied meaning difference, which can be brought out in an appropriate context. Consider happily, for instance. It is used in sentential function in (59a–c):

These sentences imply that the speaker is happy about John’s studying for the examination, without any implication that John is happy about doing this (he might be or he might not be). Now consider happily used as a manner adverb, in (60a–b).
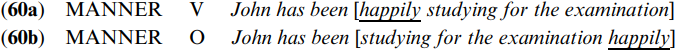
These sentences state that John is studying in a happy mode.
Most adverbs retain the same meaning but just provide different kinds of modification when used in sentential and in manner functions. For example, sensibly means ‘it is sensible to do it’ in sentential and ‘it is done in a sensible way’ in manner function. But for some adverbs there is a slight meaning difference between the two functions. This was illustrated for quietly at (18a–b) and for honestly at (19a–b); it was there noted that frankly shows a similar difference.
Set (3) consists of adverbs from the CORRECT subset of the QUALIFICATION type of adjectives—correctly, rightly, wrongly, appropriately, and sensibly (mentioned in the preceding paragraph). These behave in a similar way to adverbs in set (2). For example, correctly could be substituted for stupidly in (13a–c)—stating that the soldier was correct to offer an answer to the question—and in (14a–b)—stating that he provided the correct answer. Adverbs from sets (2) and (3) may also modify an adjective (for example, stupidly anxious, appropriately diligent).
Set (4) consists just of similarly. This generally relates to something preceding in discourse. Suppose one person says Mary has been making a model. Someone else could reply, using any of:

Sentences (61a–c) state that John has been doing a similar thing to Mary, making a model. In contrast, (62) says that he has been making a model in a similar manner to Mary. It appears that, in manner function, similarly is restricted to position O. Similarly may also modify an adjective or an adverb; for example, similarly clever(ly).
The other items in the SIMILARITY semantic type do not pattern in this way. Differently simply functions as manner adverb in position O. Separately and independently function as manner adverbs in positions V and O. Adjectives like and unlike do not form adverbs since in modern English there already exist forms likely and unlikely with quite different meanings.
Set (5) involves adverbs derived from adjectives of the SPEED semantic type—slowly, quickly, rapidly, speedily and also fast (where adjective and adverb have the same form). These may occur in the three sentential and two manner positions. Of all the adverbs, these pose the most difficulty for perceiving distinct sentential and manner function senses. It seems that the manner positions are used to describe the speed of a volitional action; for example, She has been [(slowly) writing her memoirs (slowly)]. And the sentential positions may be preferred to describe the speed at which something happens; for example, (Slowly) she has (slowly) been gaining in confidence (slowly). These adverbs are unlikely to occur with LIKING verbs; and they do not easily modify adjectives or adverbs.
 الاكثر قراءة في Semantics
الاكثر قراءة في Semantics
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















