

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Adjectives modifying nouns
المؤلف:
Patrick Griffiths
المصدر:
An Introduction to English Semantics And Pragmatics
الجزء والصفحة:
36-2
11-2-2022
1860
Adjectives modifying nouns
How are noun and adjective meanings put together when an adjective modifies a noun as in green bicycles? Just enough will be said here to show that interesting issues arise in this area. A simple interpretation in terms of the intersection of sets, as depicted in Figure 2.3, will work in some cases.
In Figure 2.3, the left-hand oval represents the set denoted by green, all the green entities that there could be. The right-hand oval represents the set of entities denoted by bicycle, all bicycles.

The intersection of the two ovals encompasses things that are included in both sets, things that are green and also bicycles. This is a satisfactory enough account of how these two meanings are put together. Adjectives that fit this scheme of interpretation are called intersective adjectives.
Some adjectives are straightforwardly non-intersective: former, imaginary, fake. Former champions are no longer denoted in an uncomplicated way by the word champion; a fake Stradivarius is not a Stradivarius. Lappin (2001) gives a short overview of some proposals in formal semantics for handling such cases.
Two further types of non-intersective modification will be mentioned here. One class arises from what can be called relative adjectives (Cruse 2000: 290). Two examples are given in (2.23).
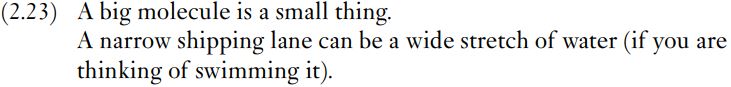
The problem for an intersective account of modification with small or big, wide or narrow, or any of numerous other relative adjectives is that the adjective is interpreted relative to the norms of the entities denoted by the noun: ‘big as molecules go’, ‘narrow when compared to an average shipping lane’.
Another set of cases where an intersective explanation of modification is not feasible is illustrated by the ambiguity of (2.24).
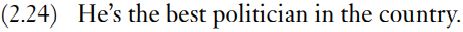
One can use (2.24) either to describe someone who is skilled at politicking, whether or not one approves of him as a person, or of someone who is good and happens to be a politician, whether or not he is competent in the practice of politics. The first meaning appears to rely on there being characteristic roles, duties, activities or functions for certain classes of people: a politician engages in politics, an embroiderer embroiders, a farmer farms, a plumber installs and repairs water systems. Now some adjectives can be taken as qualifying the extent to which the characteristic role is carried out (on this reading the best politician is the one who practises politics best). There is an ambiguity if the same adjective could also be used to describe the nature of people as people (the best politician could be understood as the most virtuous one). When the noun denotes something inanimate, then the only interpretation is likely to be the one in which its function is qualified by the adjective, for example a good shovel is one that is better than averagely suited for shovelling.
 الاكثر قراءة في Semantics
الاكثر قراءة في Semantics
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















