
Adaptive Histogramming (Variable-Partition Histogramming)
 المؤلف:
Garnett P. Williams
المؤلف:
Garnett P. Williams
 المصدر:
Chaos Theory Tamed
المصدر:
Chaos Theory Tamed
 الجزء والصفحة:
63
الجزء والصفحة:
63
 10-3-2021
10-3-2021
 2816
2816
Adaptive Histogramming (Variable-Partition Histogramming)
Data are often unevenly distributed over a frequency distribution. For example, they might be sparse in the tails (and sometimes elsewhere) and more numerous in the middle. A fixed bin width then might result in much of the information being swallowed up by one bin. Other regions might have isolated bins (isolated probability estimates), and still others might have zero probability. At least theoretically, such isolated estimates interrupt the continuity of the final probability density distribution (an undesirable result). To cope with that problem, statisticians developed a group of techniques that are data-sensitive or data-adaptive. That means they don't apply the same bin width to the entire distribution. Instead, the methods change bin (partition) width from one bin to another according to local peculiarities (especially number of observations) in the data. They adapt the amount of smoothing to the local density of data. They do so by using wide bins for ranges that have only a few data points (typically the tails of the frequency distribution) but narrow bins for ranges that contain many points. Equation 1 still applies, but the denominator (class width) varies from one class to another. In the world of general statistics, the two most common approaches to adaptive histogramming are combining bins in the tails of the distribution (where observations tend to be fewer) or defining bin boundaries such that all bins contain the same number of data points (Scott 1992: 67). A prominent example of adaptive histogramming within chaos theory is that of Fraser & Swinney (1986). They cover the phase space with a grid in which the size of each bin depends on the number of points in the local neighborhood. Bins are smaller where there are more points, and vice versa.
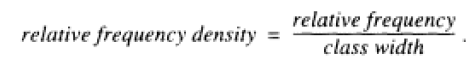 ......(1)
......(1)
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


