
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
The photomultiplier: Photon-counting photometry
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 297
25-8-2020
1879
The photomultiplier: Photon-counting photometry
The current which is measured by DC amplification represents the average flow of electrons from the anode of the photomultiplier. The flow is made up of bursts or pulses of electrons, each one being the result of the liberation of a single photoelectron from the cathode. These pulses can be seen easily if the output from a photomultiplier is fed to an oscilloscope. Since the number of primary photoelectrons is directly proportional to the intensity falling on to the photocathode, so will be the number of pulses which is available at the anode. Hence, by measuring the rate at which the pulses appear or by counting the number of pulses in a given time, the intensity of the radiation can be determined. Since the output is digital, it is already in suitable form for acceptance by computer. Each of the pulses carries a quantity of charge which is given simply by the gain of the detector.
They behave as if generated across a capacitance and given by the stray capacitance of the cables: the lower this is, the higher is the voltage of the pulse. Hence, the voltage of the pulses may be estimated as follows. Using the value of the charge of a single electron and assuming the value of 107 for the gain of the photomultiplier, the charge carried by each pulse is given by
1·6 × 10−19 × 107 = 1·6 × 10−12 C.
Now the voltage, V, across a capacitance, C, when holding a charge, Q, is given by
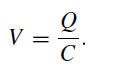
If the stray capacitance can be held to a value as low as 10−11 farad (10 picofarad), then the voltage appearing across it is given by
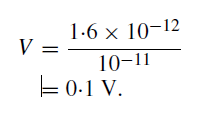
A further amplification, by means of a wide-band amplifier, is, therefore, normally required before the pulses can be counted by a scaler (see figure 1). It must also be remembered that the production of secondary electrons by the dynodes is a statistical process and that there is a range in the voltage heights of the pulses.
Photon-counting photometry lends itself to immediate assessments of the quality of any data. Successive counts over a fixed integration time will be distributed about some mean value, the photon count rate being subject to a noise sometimes referred to as shot noise. The distribution of values can be checked against that predicted by the statistics of photon counting. If the match is good, then the observations are at the limit of the best possible accuracy, with no other noise sources degrading the measurements. Under this circumstance, the fractional uncertainty (the inverse of the signal-to-noise ratio) of any photometric measurement is given by
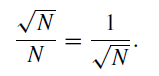
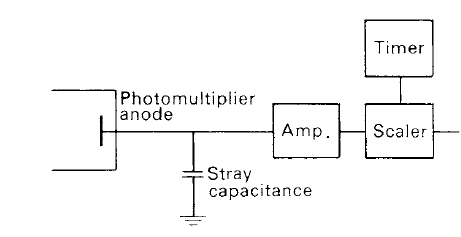
Figure1. A simple pulse counting photometer.
Hence, any record may be expressed as 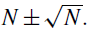 . It is easily seen, therefore, that if measurements with an accuracy of 1% are planned, it is necessary only to choose an integration time which provides a total count of N > 104; and this will depend on the brightness of the object and the aperture of the telescope. Higher accuracies can be achieved by recording greater total counts.
. It is easily seen, therefore, that if measurements with an accuracy of 1% are planned, it is necessary only to choose an integration time which provides a total count of N > 104; and this will depend on the brightness of the object and the aperture of the telescope. Higher accuracies can be achieved by recording greater total counts.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















