
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Southern hemisphere celestial spheres
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 62
22-7-2020
1834
Southern hemisphere celestial spheres
To clarify the ideas introduced in the previous sections, we consider the celestial sphere for an observer in the southern hemisphere. Let the latitude be ∅S. Then the celestial pole above the horizon is the south celestial pole Q. We proceed as follows:
1. Draw a sphere.
2. Insert the zenith, Z, and the horizon, NWSE, a great circle with Z as one of its poles.
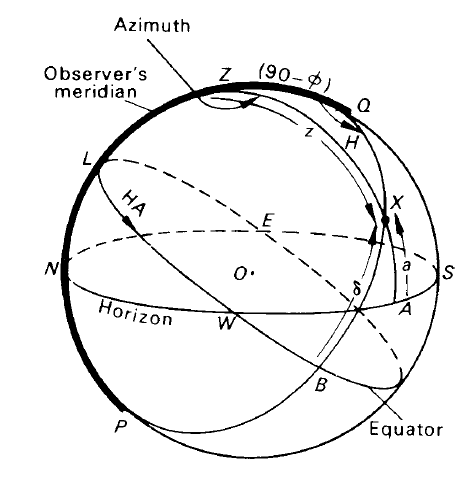
Figure 1. A southern hemisphere celestial sphere
3. In figure 1 we have placed W on the front of the diagram. The convention that when facing north, west is on your left hand dictates the placing of N, S and E.
4. Insert Q, the south celestial pole, between the south point S and the zenith Z and such that the
altitude SQ of the pole is the latitude φ of the observer. We can then insert the north celestial pole P directly opposite.
5. Put the celestial equator in the diagram, remembering that P and Q are its poles.
6. Insert the observer’s meridian QZNP, according to the rule that it runs from the pole in the sky through the zenith and horizon to the pole below the Earth.
7. Put an arrowhead on the equator with HA beside it to show that the hour angle is measured westwards from the observer’s meridian.
Let us suppose we are interested in the position of a star X.
8. Draw the vertical ZXA and the meridian QXBP through its position. Then,
the azimuth of X = arc SE A = A◦ E of S
the altitude of X = arc AX = a◦
the zenith distance of X = arc ZX = 90 − a
the declination of X = arc BX = δ◦ S
the hour angle of X = arc LB = Hh
the south polar distance of X = arc QX = 90 − δ.
Note: (a) that the azimuth is specified E of S to avoid ambiguity; (b) that the declination is labelled S again to avoid ambiguity.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















