
The retroaldol reaction
 المؤلف:
..................
المؤلف:
..................
 المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 27-11-2019
27-11-2019
 1631
1631
The retroaldol reaction
Although aldol reactions play a very important role in the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds in metabolic pathways, it is important to emphasize that they are also highly reversible: in most cases, the energy level of starting compounds and products are very close. This means that, depending on metabolic conditions, aldolases can also catalyze retro-aldol reactions (the reverse of aldol condensations, in which carbon-carbon bonds are broken). Recall that fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase is active in the direction of sugar breakdown (glycolysis) as well as sugar synthesis (gluconeogenesis). In the glycolytic direction, the enzyme catalyzes - either by zinc cation or by imine/enamine mechanisms, depending on the organism - the retro-aldol cleavage of fructose bisphosphate into DHAP and GAP.

The mechanism is the exact reverse of the condensation reaction. Shown below is the mechanism for a Zn2+ - dependent (Type II) retroaldol cleavage. Notice that in the retroaldol reaction, the enolate intermediate is the leaving group, rather than the nucleophile.
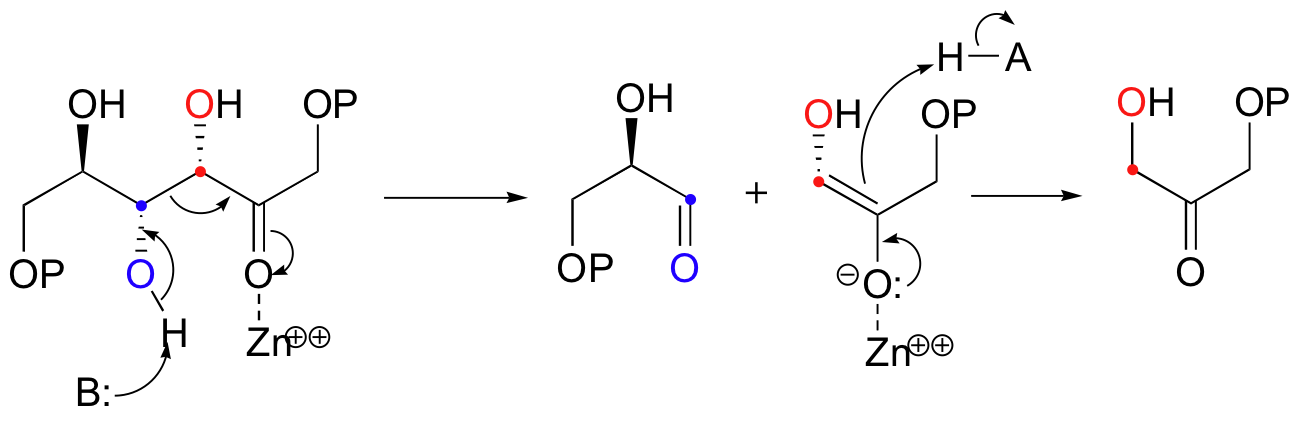
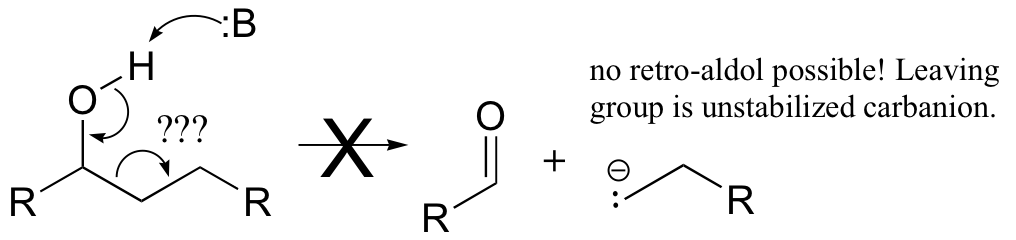
The key thing to keep in mind when looking for a possible retro-aldol mechanism is that, when the carbon-carbon bond breaks, the electrons must have some place to go, where they will be stabilized by resonance. Generally, this means that there must be a carbonyl or imine group on the next carbon. If there is no adjacent carbonyl or imine group, the carbon-carbon bond is not free to break.
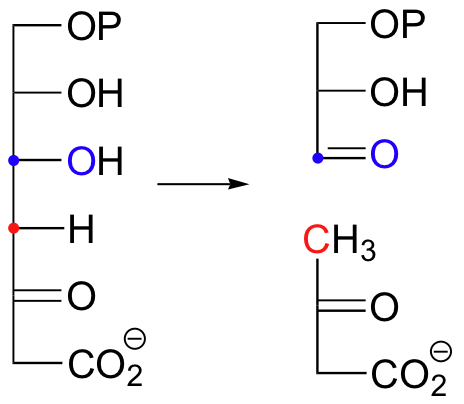
Here are two more examples of retro-aldol reactions. Bacterial carbohydrate metabolism involves this reversible, class I retro-aldol cleavage: (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2001, 98, 3679).
Another interesting example is the retro-aldol cleavage of indole-3-glycerol phosphate, a step in the biosynthesis of tryptophan.
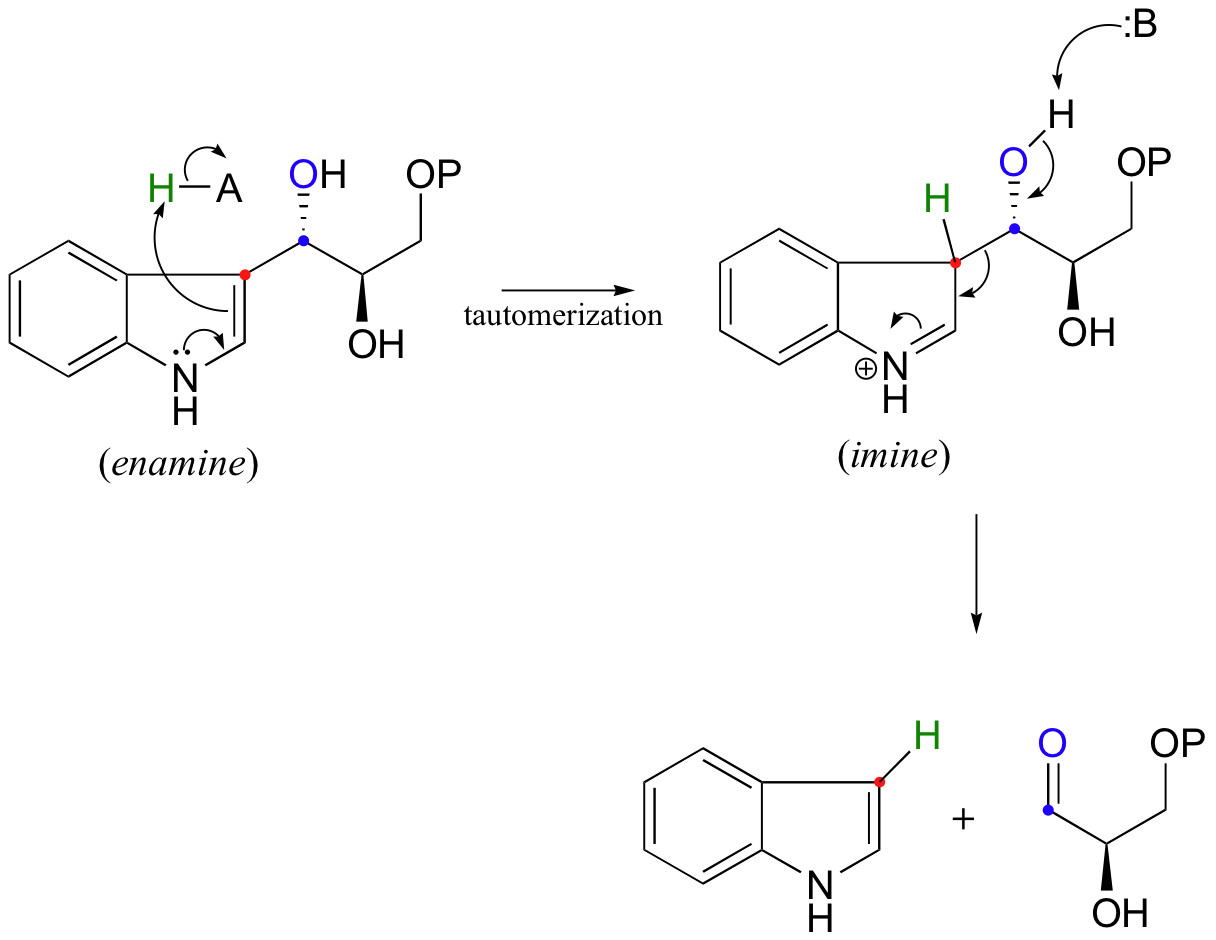
Look carefully at this reaction - how is the leaving group stabilized? There is an imine group involved, but no participation by an enzymatic lysine. The imine is 'built into' the starting compound, available from the initial tautomerization of the cyclic enamine group in indole-3-glycerol phosphate.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


