Biologic Conversion of Carboxylic Acids
In biological chemistry direct conversion of a carboxylic acid to an acyl derivative by nucleophilic acyl substitution does not occur. Rather, the first conversion is from a carboxylate (the least reactive acyl transfer substrate) to an acyl phosphate (the most reactive acyl transfer substrate). This transformation requires a reaction that we are familiar with: phosphorylation of a carboxylate oxygen with ATP as the phosphate donor.
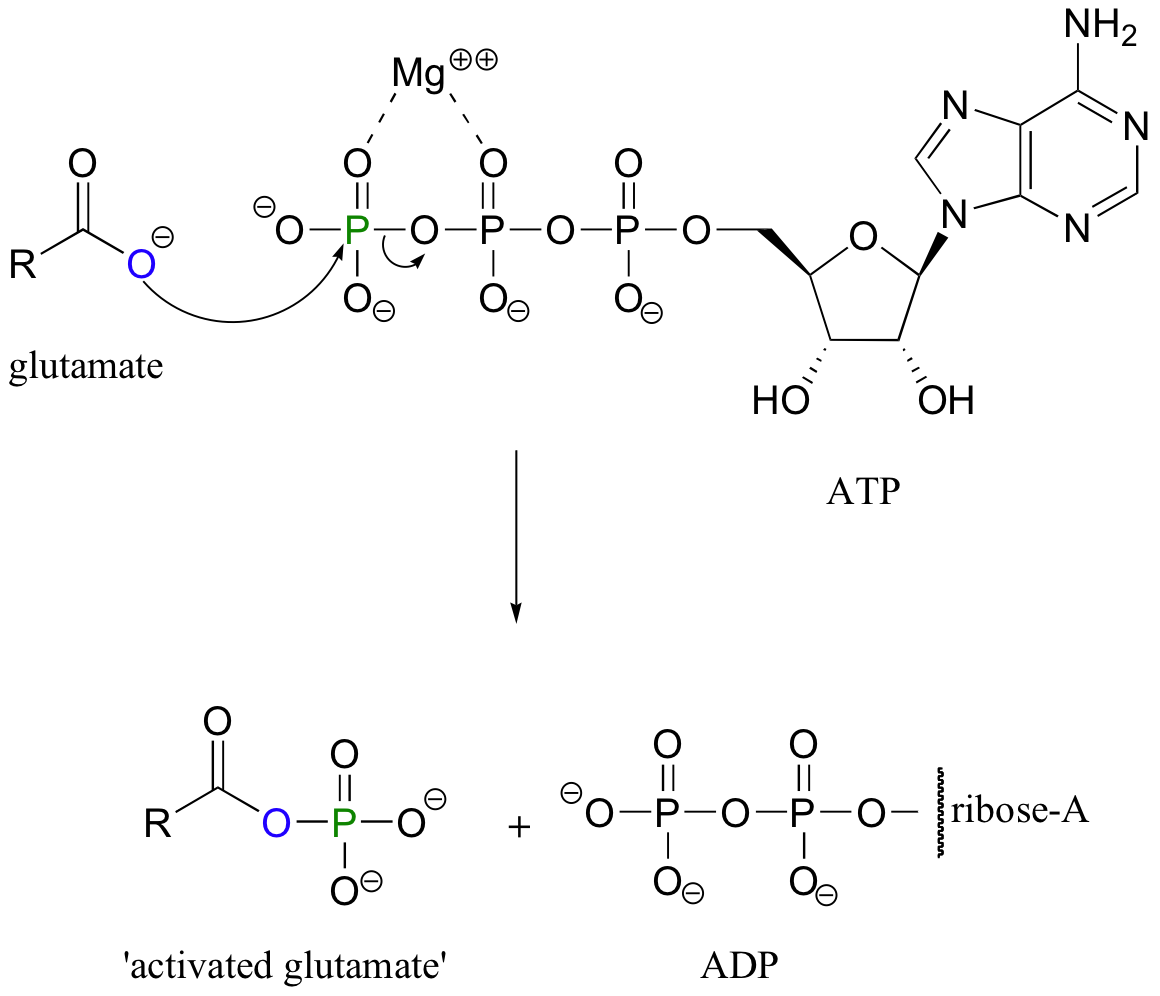
Note that this is just one of the many ways that ATP is used as a energy storage unit: in order to make a high energy acyl phosphate molecule from a low energy carboxylate, the cell must ‘spend’ the energy of one ATP molecule.
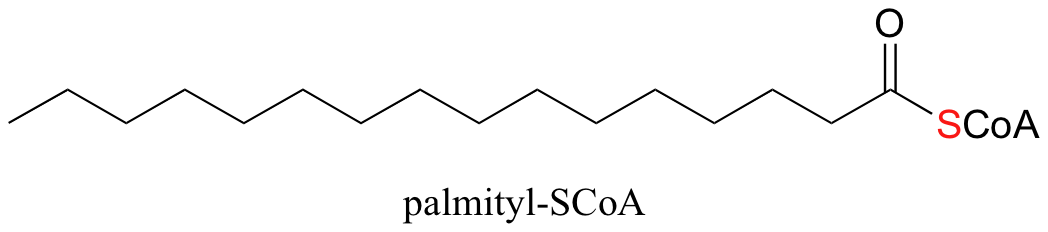
An excellent example of biological activated carboxylic acids is seed in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. In the biologically active form of fatty acids, the carboxylate groups have been converted to thioesters using coenzyme A. For example, the activated form of the C16 fatty acid palmitate is:
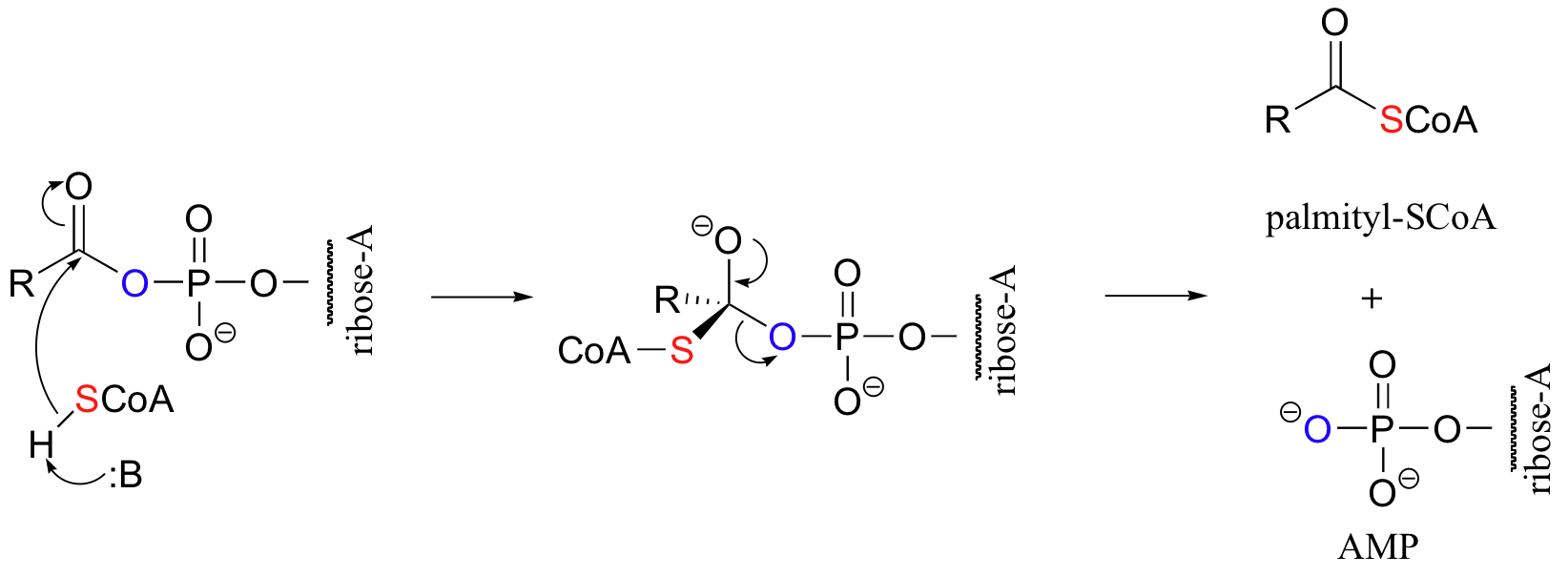
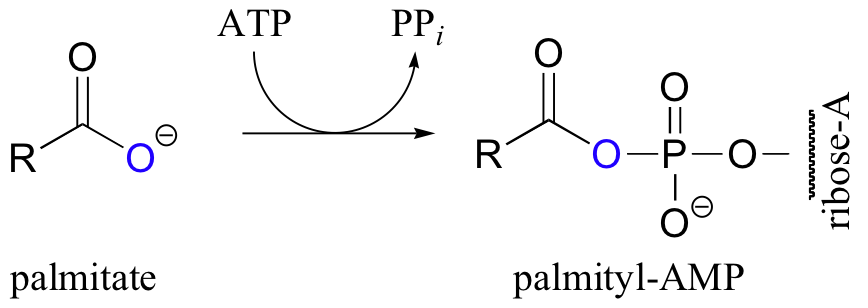
Let’s take a look at how this activation takes place, in a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme called acyl CoA synthetase. You already know that carboxylates are not themselves good substrates for acyl substitution reactions, and must be activated. Thus, you might predict that the first step of this reaction requires ATP to make a high-energy acyl phosphate intermediate. In fact, the activated carboxylate in this case is an acyl-AMP, formed in the same way as the acyl-AMP intermediate in the asparagine synthetase reaction (section 12.2B).
The activated acyl-AMP intermediate is then attacked by the thiol sulfur of coenzyme A, and the AMP group is expelled to form the fatty acyl CoA.