
Haloalkanes Have Higher Boiling Points than Alkanes
 المؤلف:
..................
المؤلف:
..................
 المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 23-7-2019
23-7-2019
 1363
1363
Haloalkanes Have Higher Boiling Points than Alkanes
When comparing alkanes and haloalkanes, we will see that haloalkanes have higher boiling points than alkanes containing the same number of carbons. London dispersion forces are the first of two types of forces that contribute to this physical property. You might recall from general chemistry that London dispersion forces increase with molecular surface area. In comparing haloalkanes with alkanes, haloalkanes exhibit an increase in surface area due to the substitution of a halogen for hydrogen. The incease in surface area leads to an increase in London dispersion forces, which then results in a higher boiling point.
Dipole-dipole interaction is the second type of force that contributes to a higher boiling point. As you may recall, this type of interaction is a coulombic attraction between the partial positive and partial negative charges that exist between carbon-halogen bonds on separate haloalkane molecules. Similar to London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions establish a higher boiling point for haloalkanes in comparison to alkanes with the same number of carbons.

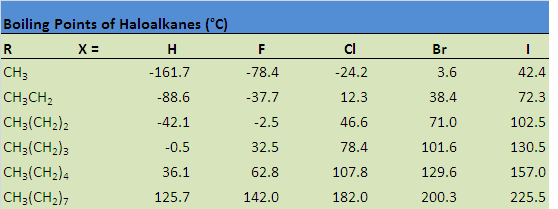
The table below illustrates how boiling points are affected by some of these properties. Notice that the boiling point increases when hydrogen is replaced by a halogen, a consequence of the increase in molecular size, as well as an increase in both London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole attractions. The boiling point also increases as a result of increasing the size of the halogen, as well as increasing the size of the carbon chain.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


