

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Formation of Imines and Related Compounds
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
1-8-2018
1718
Formation of Imines and Related Compounds
The reaction of aldehydes and ketones with ammonia or 1º-amines forms imine derivatives, also known as Schiff bases, (compounds having a C=N function). Water is eliminated in the reaction, which is acid-catalyzed and reversible in the same sense as acetal formation.
R2C=O + R'NH2  R'NH–(R2)C–O–H
R'NH–(R2)C–O–H  R2C=NR' + H2O
R2C=NR' + H2O
An addition-elimination mechanism for this reaction was proposed, and an animation showing this mechanism is activated by the button.
Imines are sometimes difficult to isolate and purify due to their sensitivity to hydrolysis. Consequently, other reagents of the type Y–NH2 have been studied, and found to give stable products (R2C=N–Y) useful in characterizing the aldehydes and ketones from which they are prepared. Some of these reagents are listed in the following table, together with the structures and names of their carbonyl reaction products. An interesting aspect of these carbonyl derivatives is that stereoisomers are possible when the R-groups of the carbonyl reactant are different. Thus, benzaldehyde forms two stereoisomeric oximes, a low-melting isomer, having the hydroxyl group cis to the aldehyde hydrogen (called syn), and a higher melting isomer in which the hydroxyl group and hydrogen are trans (the anti isomer). At room temperature or below the configuration of the double-bonded nitrogen atom is apparently fixed in one trigonal shape, unlike the rapidly interconverting pyramidal configurations of the sp3 hybridized amines.
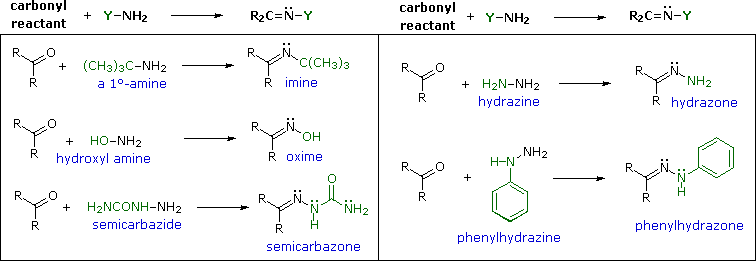
With the exception of unsubstituted hydrazones, these derivatives are easily prepared and are often crystalline solids - even when the parent aldehyde or ketone is a liquid. Since melting points can be determined more quickly and precisely than boiling points, derivatives such as these are useful for comparison and identification of carbonyl compounds. If the aromatic ring of phenylhydrazine is substituted with nitro groups at the 2- & 4-positions, the resulting reagent and the hydrazone derivatives it gives are strongly colored, making them easy to identify. It should be noted that although semicarbazide has two amino groups (–NH2) only one of them is a reactive amine.
The rate at which these imine-like compounds are formed is generally greatest near a pH of 5, and drops at higher and lower pH's. This agrees with a general acid catalysis in which the conjugate acid of the carbonyl reactant combines with a free amino group, as shown in the above animation. At high pH there will be a vanishingly low concentration of the carbonyl conjugate acid, and at low pH most of the amine reactant will be tied up as its ammonium conjugate acid. With the exception of imine formation itself, most of these derivatization reactions do not require active removal of water (not shown as a product in the previous equations). The reactions are reversible, but equilibrium is not established instantaneously and the products often precipitate from solution as they are formed.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















