

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Six-Membered Rings : Properties
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
29-7-2018
3349
Six-Membered Rings
Properties
The chemical reactivity of the saturated members of this class of heterocycles: tetrahydropyran, thiane and piperidine, resemble that of acyclic ethers, sulfides, and 2º-amines, and will not be described here. 1,3-Dioxanes and dithianes are cyclic acetals and thioacetals. These units are commonly used as protective groups for aldehydes and ketones, as well as synthetic intermediates, and may be hydrolyzed by the action of aqueous acid. The reactivity of partially unsaturated compounds depends on the relationship of the double bond and the heteroatom (e.g. 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran is an enol ether).
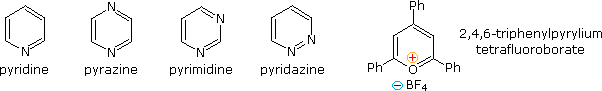
Fully unsaturated six-membered nitrogen heterocycles, such as pyridine, pyrazine, pyrimidine and pyridazine, have stable aromatic rings. Oxygen and sulfur analogs are necessarily positively charged, as in the case of 2,4,6-triphenylpyrylium tetrafluoroborate.
From heat of combustion measurements, the aromatic stabilization energy of pyridine is 21 kcal/mole. The resonance description drawn at the top of the following diagram includes charge separated structures not normally considered for benzene. The greater electronegativity of nitrogen (relative to carbon) suggests that such canonical forms may contribute to a significant degree. Indeed, the larger dipole moment of pyridine compared with piperidine supports this view. Pyridine and its derivatives are weak bases, reflecting the sp2 hybridization of the nitrogen. From the polar canonical forms shown here, it should be apparent that electron donating substituents will increase the basicity of a pyridine, and that substituents on the 2 and 4-positions will influence this basicity more than an equivalent 3-substituent. The pKa values given in the table illustrate a few of these substituent effects. Methyl substituted derivatives have the common names picoline (methyl pyridines), lutidine (dimethyl pyridines) and collidine (trimethyl pyridines). The influence of 2-substituents is complex, consisting of steric hindrance and electrostatic components. 4-Dimethylaminopyridine is a useful catalyst for acylation reactions carried out in pyridine as a solvent. At first glance, the sp3 hybridized nitrogen might appear to be the stronger base, but it should be remembered that N,N-dimethylaniline has a pKa slightly lower than that of pyridine itself. Consequently, the sp2 ring nitrogen is the site at which protonation occurs.
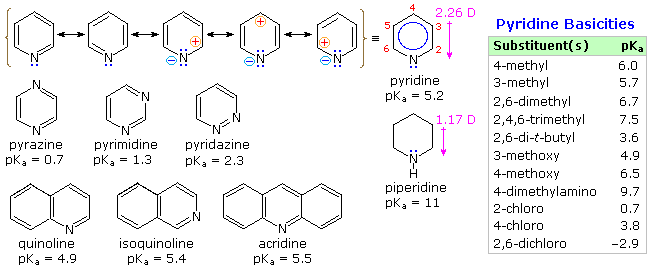
The diazines pyrazine, pyrimidine and pyridazine are all weaker bases than pyridine due to the inductive effect of the second nitrogen. However, the order of base strength is unexpected. A consideration of the polar contributors helps to explain the difference between pyrazine and pyrimidine, but the basicity of pyridazine seems anomalous. It has been suggested that electron pair repulsion involving the vicinal nitrogens destabilizes the neutral base relative to its conjugate acid.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















