
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Particle in Expanding Box
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 55
19-8-2016
1105
Particle in Expanding Box
A particle of mass m is contained in a one-dimensional impenetrable box extending from x = -L/2 to x = +L/2. The particle is in its ground state.
a) Find the eigenfunctions of the ground state and the first excited state.
b) The walls of the box are moved outward instantaneously to form a box extending from –L ≤ x ≤ L. Calculate the probability that the particle will stay in the ground state during this sudden expansion.
c) Calculate the probability that the particle jumps from the initial ground state to the first excited final state.
SOLUTION
a) For a particle confined to a box –L/2 ≤ x ≤ L/2, the ground state ѱ0(x) and the first excited state ѱ1(x) are
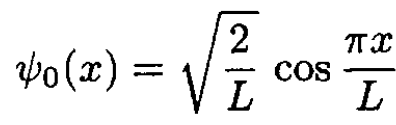 (1)
(1)
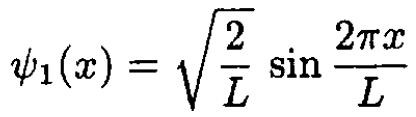 (2)
(2)
After the sudden transition L → 2L, the final eigenfunctions are
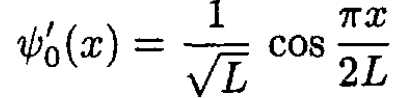 (3)
(3)
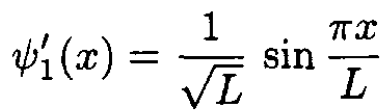 (4)
(4)
b) In the sudden approximation let P0j denote the probability that the particle starts in the ground state 0 and ends in the final state j:
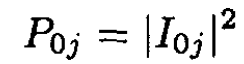 (5)
(5)
where the amplitude of the transition I0j is given by
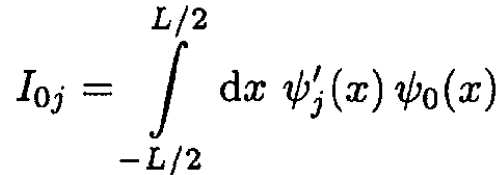 (6)
(6)
The amplitude for the particle to remain in its ground state is then
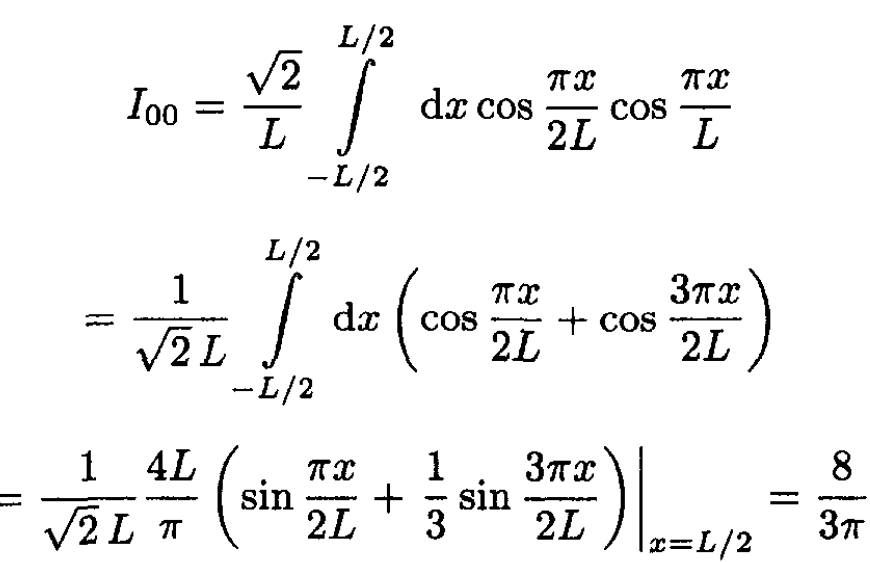 (7)
(7)
The probability P00 is given by
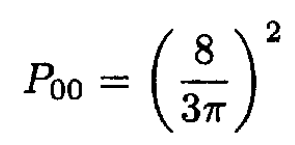 (8)
(8)
The same calculation for the transition between the initial ground state and final excited state ѱ'1 is as follows:
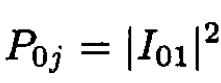 (9)
(9)
where
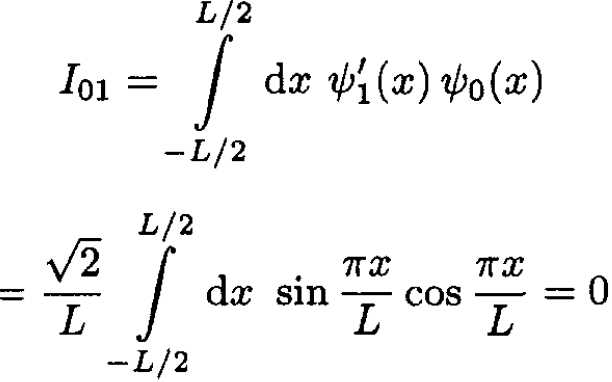 (10)
(10)
The integral is zero by parity, since the integrand is an odd function of x, so
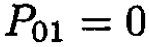 (11)
(11)