
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Cut the Spring!
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 60
14-8-2016
1186
Cut the Spring!
A particle is allowed to move in one dimension. It is initially coupled to two identical harmonic springs, each with spring constant K. The springs are symmetrically fixed to the points ±a so that when the particle is at x = 0
the classical force on it is zero.
a) What are the eigenvalues of the particle while it is connected to both springs?
b) What is the wave function in the ground state?
c) One spring is suddenly cut, leaving the particle bound to only the other one. If the particle is in the ground state before the spring is cut, what is the probability it is still in the ground state after the spring is cut?
SOLUTION
a) Below we give the Hamiltonian H2, the frequency ω2, and the eigenvalues E(2)n of the particle while coupled to two springs:
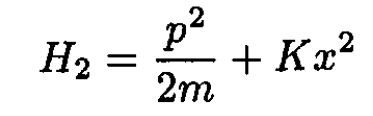 (1)
(1)
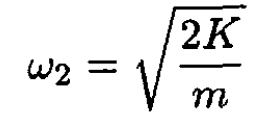 (2)
(2)
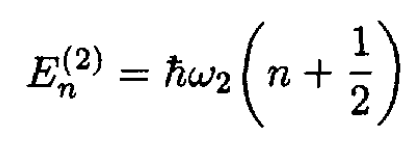 (3)
(3)
The only change from the harmonic oscillator for a single spring is that, with two identical springs, the effective spring constant is 2K.
b) The eigenfunction of the ground state (n = 0) is
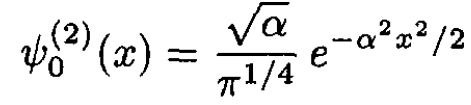 (4)
(4)
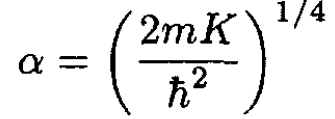 (5)
(5)
c) When one spring is cut, the particle is now coupled to only a single spring. So we must replace 2K in the above equations by K. The ground state eigenfunction is now
 (6)
(6)
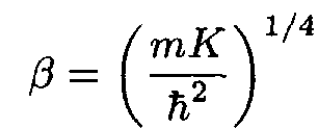 (7)
(7)
Notice that β = α/21/4. The amplitude I for remaining in the ground state is found, in the sudden approximation, by taking the overlap integral of the two ground state wave functions. The probability P00' of remaining in the ground state is the square of this overlap integral:
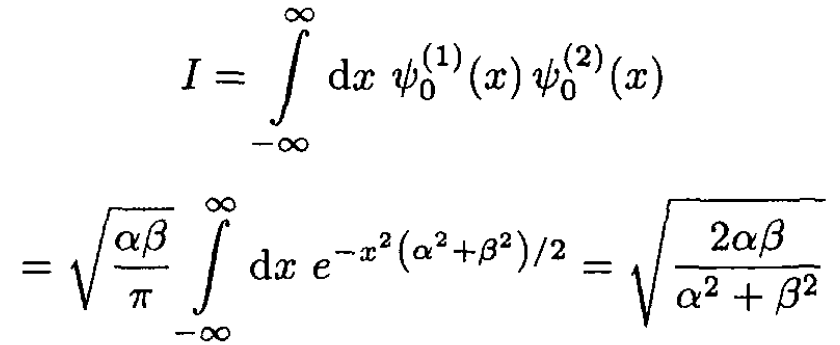 (8)
(8)
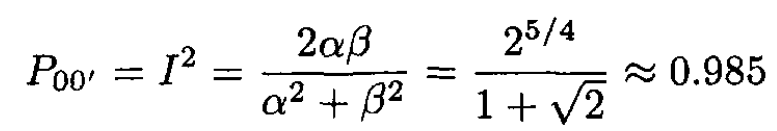 (9)
(9)
where we have used β = α/21/4 in deriving the last line. The probability of remaining in the ground state is close to unity.