
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Attractive Delta Function Potential II
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 53
14-8-2016
1473
Attractive Delta Function Potential II
A particle of mass m is confined to the right half-space, in one dimension, by an infinite potential at the origin. There is also an attractive delta function potential V(x) = -V0 aδ(x – a), where a > 0 (see Figure 1.1).
a) Find the expression for the energy of the bound state.
b) What is the minimum value of V0 required for a bound state?
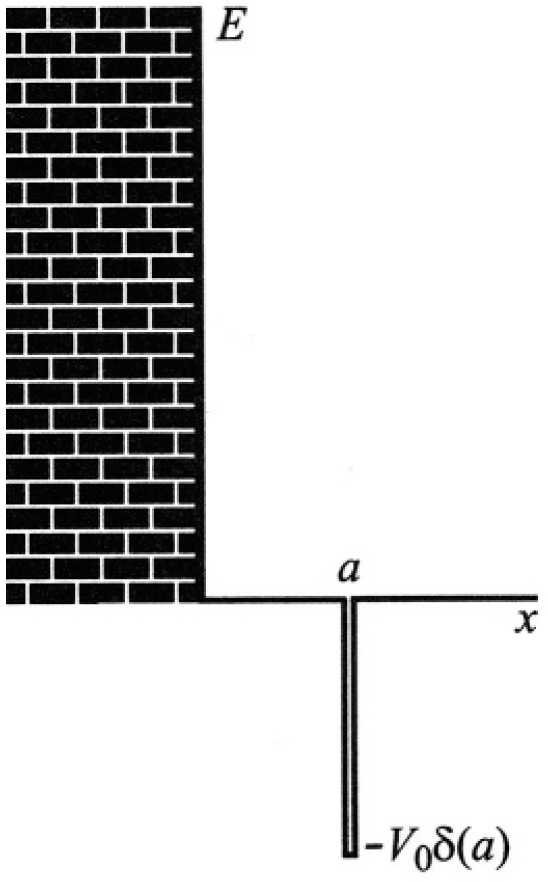
Figure 1.1
SOLUTION
a) In order to construct the wave function for the bound state, we first review its properties. It must vanish at the point x = 0. At the point x = a, it is continuous:
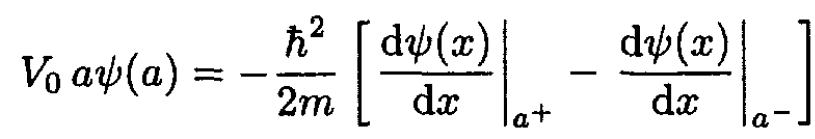 (1)
(1)
Away from the points x = (0, a) it has an energy E = -h2α2/2m and wave functions that are combinations of e-αx and eαx. These constraints dictate that the eigenfunction has the form
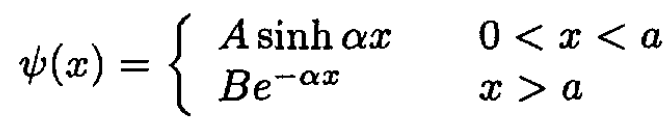 (2)
(2)
At the point x = a, we match the two eigenfunctions and their derivatives, using (1). This yields two equations, which are solved to find an equation for α:
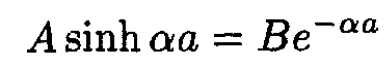 (3)
(3)
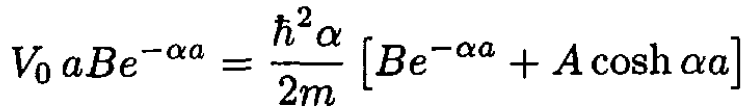 (4)
(4)
We use the first equation to eliminate A in the second equation. Then each term has a factor of Be-αa which is canceled:
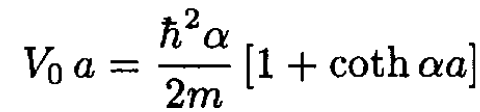 (5)
(5)
Multiplying both sides of (5) by sinh αa gives
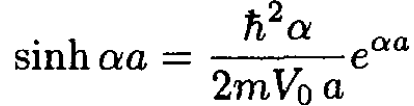 (6)
(6)
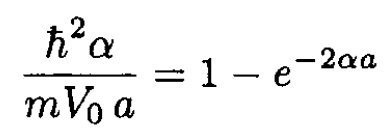 (7)
(7)
This last equation determines α, which determines the bound state energy. There is only one solution for sufficiently large values of V0.
b) The minimum value of V0 for creating a bound state is called Vc. It is found by assuming that the binding energy E → 0, which means α → 0. We examine (7) for small values of α and find that
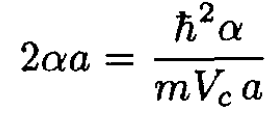 (8)
(8)
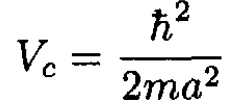 (9)
(9)