
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Magnetic Dipole and Permeable Medium
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 60
9-8-2016
1452
Magnetic Dipole and Permeable Medium
A point magnetic dipole m in vacuum (medium 1) is pointing toward the plane surface of a medium with permeability μ (medium 2). The distance between the dipole and surface is d (see Figure 1.1).
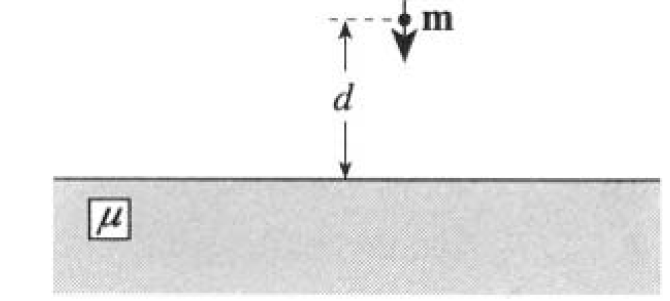
Figure 1.1
a) Solve for the magnetic field B within the medium.
b) What is the force acting on the dipole?
SOLUTION
a) Use the method of images. We place another dipole m' = α m at the point O', at the same distance d on the other side of the plane separating the vacuum from the permeable medium (see Figure 1.2). Compute the field in medium 1 as a superposition of the dipole fields from m and m'. To find the field in medium 2, we put yet another dipole m'' = β m at point O. We can write this in the form
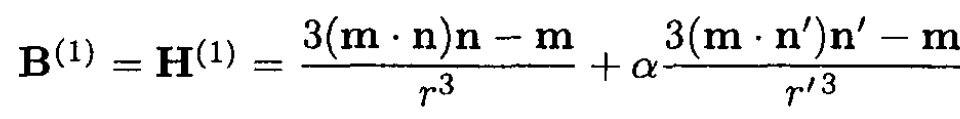 (1)
(1)
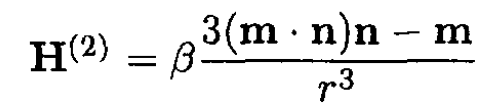 (2)
(2)
where n, n' are unit vectors in the directions r, r' respectively, and indices 1 and 2 correspond to media 1 and 2. As usual, we write the boundary
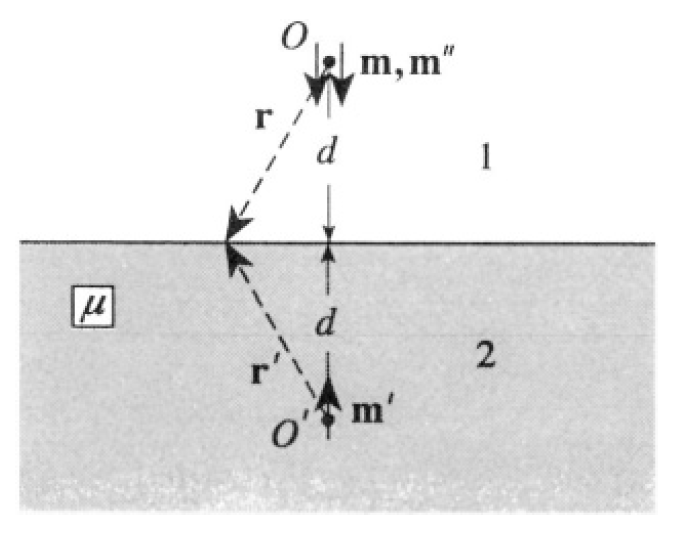
Figure 1.2
conditions at some point P on the plane where |r| = |r'|
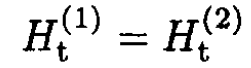 (3)
(3)
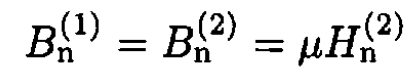 (4)
(4)
Substituting (1) and (2) into (3) and (4), we obtain
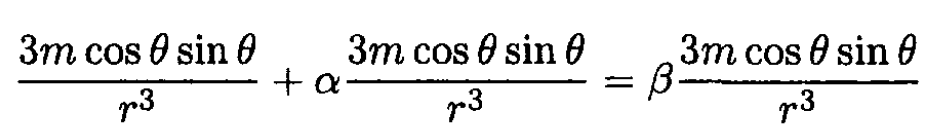 (5)
(5)
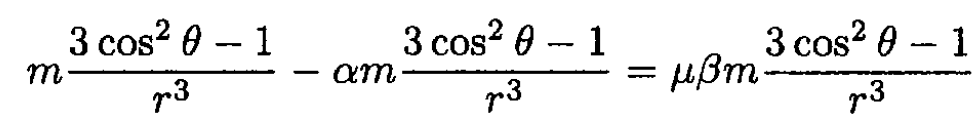 (6)
(6)
From (5) and (6), we have
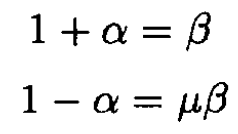 (7)
(7)
which yield
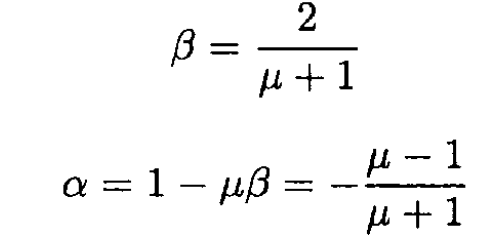
So the field in medium 2 is
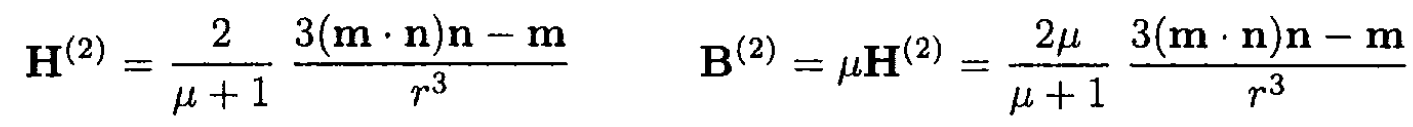
b) The force acting on a dipole m is determined only by the field B(1)' of the image dipole m' in medium 2
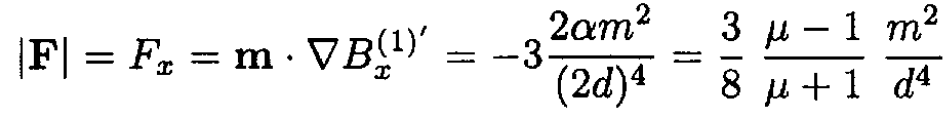 (8)
(8)
The dipole is attracted to the medium. The result for the equivalent problem of an electric dipole near a half space filled with an ideal conductor can be obtained from (8) by letting μ → ∞
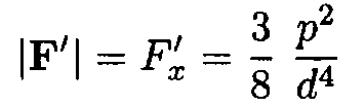
where p is the electric dipole moment.