
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Charge in Uniform Electric Field
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 37
13-7-2016
1476
Charge in Uniform Electric Field
Find the trajectory of a particle of mass m, charge e, in a uniform electric field E, assuming zero velocity parallel to E at t = 0. Sketch the trajectory in the plane of motion.
SOLUTION
The plane of motion of a particle will be defined by its initial velocity v and the direction of the electric field E. Let the initial velocity coincide with the x axis and E with the y axis. We may write the equations of motion for a charge in an electric field
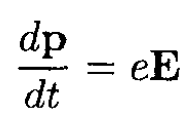 (1)
(1)
where p is the momentum of the particle. Obviously, since there is no force in the direction perpendicular to the x - y plane, the particle will move in this plane at all later times. We can write (1) in the form
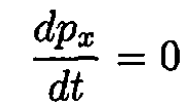 (2)
(2)
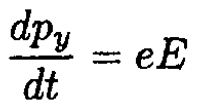 (3)
(3)
Integrating (2) and (3) yields
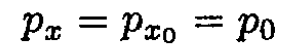 (4)
(4)
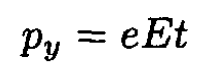 (5)
(5)
The energy ε of the particle (without the potential energy due to the field) is given by
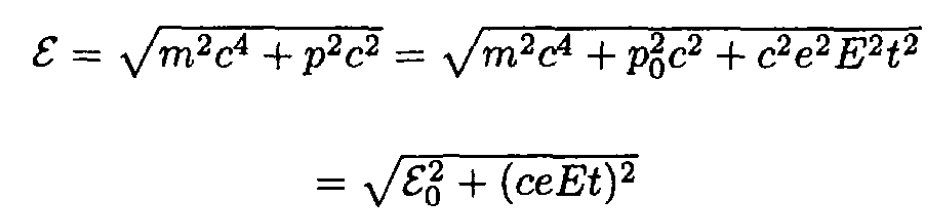 (6)
(6)
where 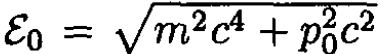 is the initial energy of the particle. The work done by the electric field changes the energy of the particle
is the initial energy of the particle. The work done by the electric field changes the energy of the particle
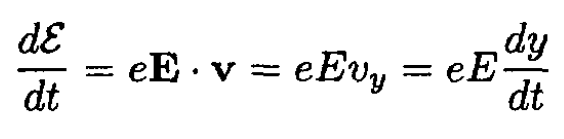 (7)
(7)
or
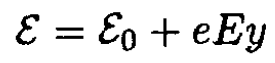 (8)
(8)
Equations (6) and (8) result in
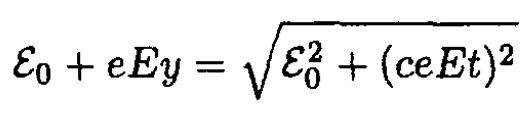 (9)
(9)
which yields
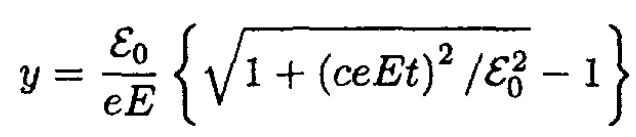 (10)
(10)
and
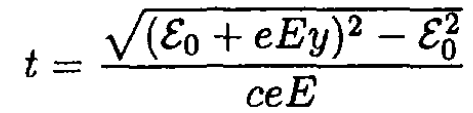 (11)
(11)
On the other hand
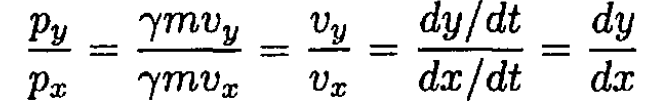 (12)
(12)
Substituting px = py and py = eEt into (12) and using t from (11), we find
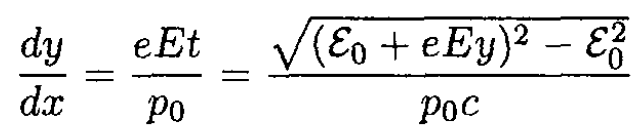 (13)
(13)
Integrating (13), we obtain
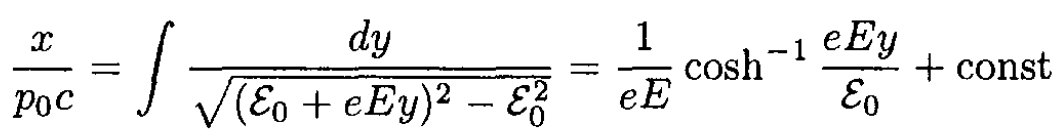
For the initial conditions x0 = y0 = 0
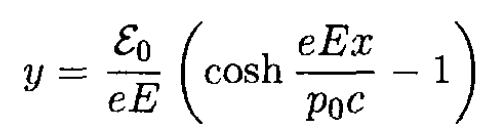 (14)
(14)
So the particle in a constant electric field moves along a catenary (see Figure 1.1, where we took e > 0). If the velocity of the particle v << c, then p0 = mv0, ε0 = mc2 and expanding cosh (eEx/p0c), we obtain
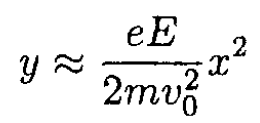
which gives the classical result for a charged particle in an electric field. Also note that (10) coincides with the result for uniformly accelerated motion in the proper reference frame, where the acceleration ω0 = eE/m and p0 = 0. Under Lorentz transformations for frames moving with velocities parallel to the electric field E, the field is unchanged.
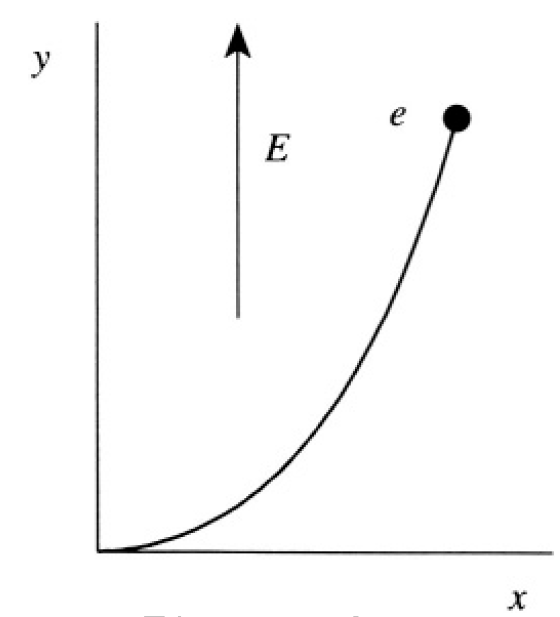
Figure 1.1