
Recommending Changes to a Structure
 المؤلف:
BARBARA MINTO
المؤلف:
BARBARA MINTO
 المصدر:
THE MINTO PYRAMID PRINCIPLE
المصدر:
THE MINTO PYRAMID PRINCIPLE
 الجزء والصفحة:
85-6
الجزء والصفحة:
85-6
 2024-09-13
2024-09-13
 889
889
Recommending Changes to a Structure
Visualizing a process in relationship to a structure is a common device, particularly if you are writing to recommend changes to an existing structure. Suppose, for example, you had the structure of a city government shown here, with 25 departments reporting to 23 committees ...
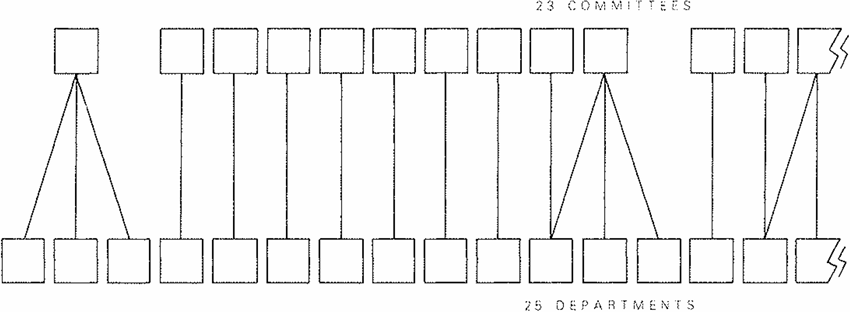
.. and you were recommending replacing it with that shown here, of essentially 6 departments reporting to 6 committees, with an administrative arm.
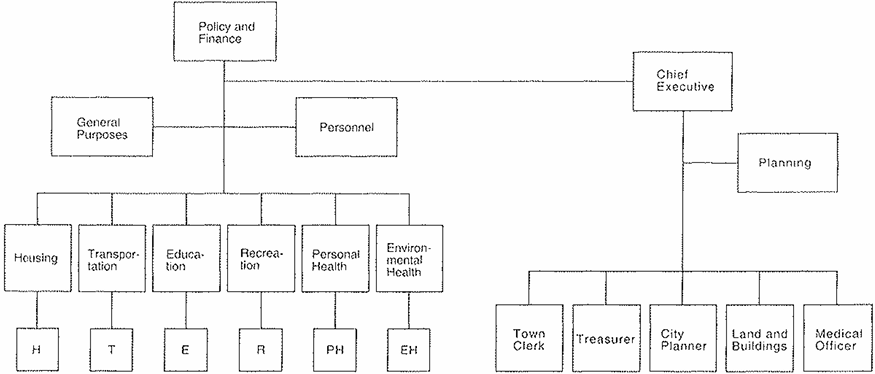
It requires four changes to get from the first structure to the second. In what order should you state them as recommendations in a report? They are all equally important, so you cannot put them in order of importance. They must, in theory, all be done at the same time, so that time order is not appropriate.
The order that makes most sense in a case like this is the order in which you would draw the elements on a blank sheet of paper if you were presenting them to the reader one at a time. Thus, the first step would be to group the many committees into the six shown on the left under a Policy and Finance Committee. The second step would be to group the departments to match. The third step would be to create the two units that will support the P&F Committee. And the final one would be to create the administrative team, under a Chief Executive, needed to manage the paperwork.
The actual wording in a final report would be as follows:
To improve the City's system of management and to enable it to perform its important tasks more effectively, the Council should take the following actions:
1. Assign responsibility for direct services to the people to six committees, under a Policy and Finance Committee
2. Croup departments into six program administrations, each under a program director to match the Committee structure
3. Structure administrative and other internal services by
-Creating a General Purposes Committee
-Directing the Personnel Committee into a more positive role designed to improve the motivation and spirit of city workers
4. Appoint a Chief Executive to be head of the City’s permanent staff
 الاكثر قراءة في Writing
الاكثر قراءة في Writing
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


