

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Koinés
المؤلف:
David Hornsby
المصدر:
Linguistics A complete introduction
الجزء والصفحة:
280-13
2024-01-04
2497
Koinés
Koinés are new compromise varieties which emerge from contact between speakers of different varieties. Koinéization is driven primarily by two processes:
• Levelling – the retention of forms which are used by a large number of speakers
• Simplification – the retention of forms which are morphologically simple or more regular, and therefore easier for post-adolescent learners to acquire.
Two other contact outcomes need also to be mentioned. In the first, incomplete accommodation between speakers of different dialects results in the creation of interdialect forms. In northern France, for example, contact between speakers of dialect and standard French has produced new compromise regional French forms, which were present in neither:
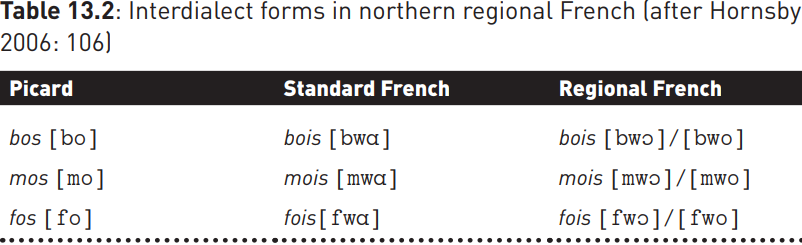
A similar compromise is evident in the lexical interdialect form take out, used in north-western England and the Midlands for a meal bought to be consumed off the premises. This form combines one element of the southern variant take away and one from the Scottish/north-eastern form carry out.
Finally, instead of being lost in the reduction process, variants can be reallocated to a new status. Trudgill suggests that this has happened in Norwich with three different variants of the ROOM vowel, originally associated with different parts of Norfolk:

The population of Norwich grew exponentially during the nineteenth century, drawing in migrants from the rural hinterland, and bringing all of these Norfolk variants to the urban dialect mix. None, however, won out over the others: instead they were reallocated as social status markers within the city. The west Norfolk [u:] form, which corresponds to that of RP, has the highest status of the three, followed by south Norfolk 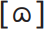 and finally the low-status north and east Norfolk form
and finally the low-status north and east Norfolk form  .
.
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonetics
الاكثر قراءة في Phonetics
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















