

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Terpene Biosynthesis
المؤلف:
LibreTexts project
المصدر:
........
الجزء والصفحة:
........
18-12-2021
2801
Terpene Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of terpenes clearly follows a somewhat different course from fatty acids in that branched-chain compounds are formed. One way that this can come about is for 2-oxobutanoyl coenzyme A to undergo an aldol addition at the keto carbonyl group with the ethanoyl coenzyme A to give the 3-methyl-3-hydroxypentanedioic acid derivative, 88:
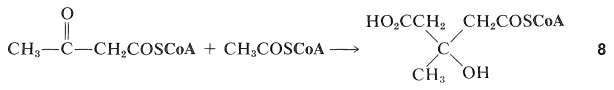
The next step is reduction of one of the carboxyl groups of 88 to give mevalonic acid:
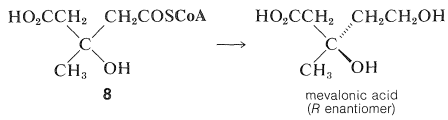
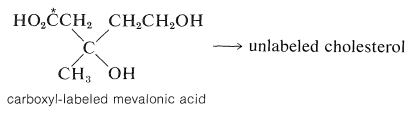
This substance has been shown by tracer studies to be an efficient precursor of terpenes and steroids. Mevalonic acid has six carbon atoms, whereas the isoprene unit has only five. Therefore, if mevalonic acid is the precursor of isoprene units, it must lose one carbon atom at some stage. Synthesis of mevalonic acid labeled at the carboxyl group with C14C14, and use of this material as a starting material for production of cholesterol, gives unlabeled cholesterol. Therefore, the carboxyl carbon is the one that is lost:
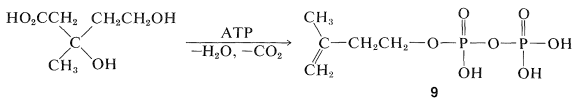
Formation of the "biological isoprene unit" from mevalonic acid has been shown to proceed by stepwise phosphorylation of both alcohol groups, then elimination and decarboxylation to yield 3-methyl-3-butenyl pyrophosphate, 9 (often called Δ3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate):
The coupling of the five-carbon units, 9, to give isoprenoid compounds has been suggested to proceed by the following steps. First, isomerization of the double bond is effected by an enzyme (E) carrying an SH group:
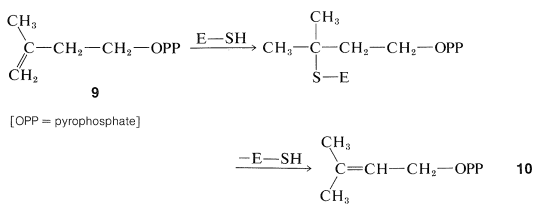
The ester, 10, then becomes connected to the double bond of a molecule of 99, probably in an enzyme-induced carbocation type of polymerization :
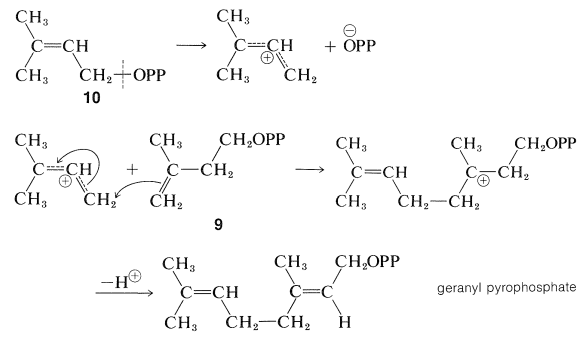
The product of the combination of two units of the pyrophosphate, 9, through this sequence is geranyl pyrophosphate if, as shown, the proton is lost to give a trans double bond. Formation of a cis double bond would give neryl pyrophosphate .
Continuation of the head-to-tail addition of five-carbon units to geranyl (or neryl) pyrophosphate can proceed in the same way to farnesyl pyrophosphate and so to gutta-percha (or natural rubber). At some stage, a new process must be involved because, although many isoprenoid compounds are head-to-tail type polymers of isoprene, others, such as squalene, lycopene, and β- and γ-carotene (Table 30-1), are formed differently. Squalene, for example, has a structure formed from head-to-head reductive coupling of two farnesyl pyrophosphates:
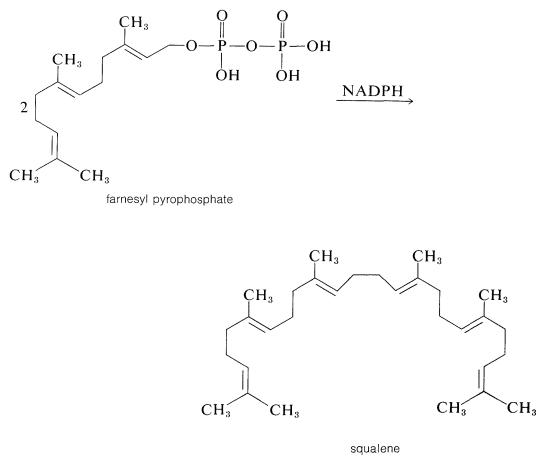
Since squalene can be produced from farnesyl pyrophosphate with NADPHNADPH and a suitable enzyme system, the general features of the above scheme for terpene biosynthesis are well supported by experiment.In summary, the sequence from ethanoate to squalene has been traced as
ethanoyl coenzyme A→mevalonic acid→isopentenyl pyrophosphate→farnesyl pyrophosphate→ squalene (30.5.4)
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















