
Antiferromagnetic resonance
 المؤلف:
J. M. D. COEY
المؤلف:
J. M. D. COEY
 المصدر:
Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
المصدر:
Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
 الجزء والصفحة:
315
الجزء والصفحة:
315
 1-3-2021
1-3-2021
 2399
2399
Antiferromagnetic resonance
An antiferromagnet is composed of two equal and opposite sublattices, each of which is subject to an anisotropy field and an exchange field. The exchange field on the ‘A’ sublattice, for example, is HexA = −nABMB , where nAB is the molecular field coefficient. Solving the equations of motion for mx,my for the two sublattices leads to the solution
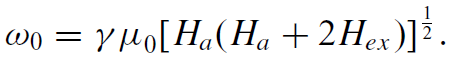
Molecular field coefficients may take values of up to 100 T in antiferromagnets, so the resonance frequencies are very high, often in the 102–103 GHz range.
 الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


