
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Domain theory
المؤلف:
J. M. D. COEY
المصدر:
Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
الجزء والصفحة:
240
23-2-2021
1778
Domain theory
The micromagnetic approach is capable, in principle, of predicting the equilibrium magnetic configurations of any system where the exchange stiffness A(r)
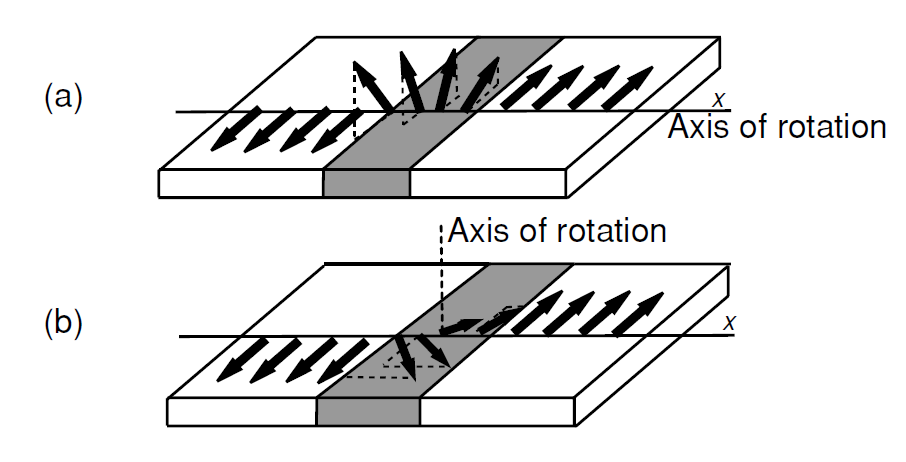
Figure 1: (a) A Bloch wall, and (b) a N´eel wall.
and anisotropy Ea(r) can be specified throughout. Hysteresis may be deduced, knowing the magnetic history in an applied field H'(t ). No account is taken of temperature. It is impractical to implement micromagnetic theory in any but idealized situations. The problem is mathematically complex, and real materials contain local defects and disorder which cannot be specified precisely, but which nonetheless tend to dominate the magnetization process.
Domain theory is an attempt to reduce this complexity to manageable proportions. It postulates the existence of large regions of uniform magnetization in a macroscopic sample, which are separated by planar regions – the domain walls – where the magnetization rotates from one easy direction to another. Domain observations support the model. If domains exist, so must domain walls. An applied field changes the net magnetization of the sample, either by causing the walls to move or by making the magnetization in the domains rotate towards the applied field direction. The magnetostatic energy depends on the wall positions and the domain orientations.
Domain theory breaks down in very soft magnetic materials, especially in thin film elements where the demagnetizing field is small. There, instead of domains, states with continuous rotation of magnetization tend to form.
Now we look more carefully into the structure of the domain walls. A flip of magnetization from one plane of atoms to the next would be prohibitively expensive, costing 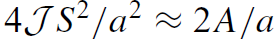 or about 0.1 Jm−2. Magnetization rotates continuously over many interatomic distances under the combined influence of exchange and anisotropy. Dimensional analysis gives the wall width
or about 0.1 Jm−2. Magnetization rotates continuously over many interatomic distances under the combined influence of exchange and anisotropy. Dimensional analysis gives the wall width 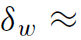
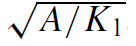 ,which is of order 10–100 nm, and thewall energy
,which is of order 10–100 nm, and thewall energy 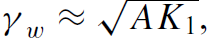 ,which is of order 1 mJ m−2. The association of energy with the wall area means that the domain wall behaves like an elastic membrane or soap film. Two common types of domain wall are illustrated in Fig. 1.
,which is of order 1 mJ m−2. The association of energy with the wall area means that the domain wall behaves like an elastic membrane or soap film. Two common types of domain wall are illustrated in Fig. 1.
 الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















