
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
PHOTOVOLTAIC (PV) CELLS
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
الجزء والصفحة:
404
21-10-2020
1610
PHOTOVOLTAIC (PV) CELLS
Some types of silicon diodes can generate dc all by themselves if sufficient IR, visible-light, or UV energy strikes their p-n junctions. This is known as the photovoltaic effect, and it is the principle by which solar cells work. Photovoltaic (PV) cells have large p-n junction surface area (Fig. 1).
This maximizes the amount of energy that strikes the junction after passing through the thin layer of p-type material. A single silicon PV cell produces approximately 0.6 V dc in direct sunlight under no-load conditions (that is, when there is nothing connected to it that will draw current from it). The maximum amount of current that a PV cell can deliver depends on the surface area of the p-n junction.
Silicon PV cells are connected in series-parallel combinations to provide solar power for solid-state electronic devices such as portable radios. A large assembly of such cells constitutes a solar panel. The dc voltages of the cells add when they are connected in series. A typical solar battery supplies 6, 9, or 12 V dc. When two or more identical sets of series-connected PV cells are connected in parallel, the output voltage is not increased, but the solar battery becomes capable of delivering more current. The currentdelivering capacity increases in direct proportion to the number of sets of series-connected cells that are connected in parallel.
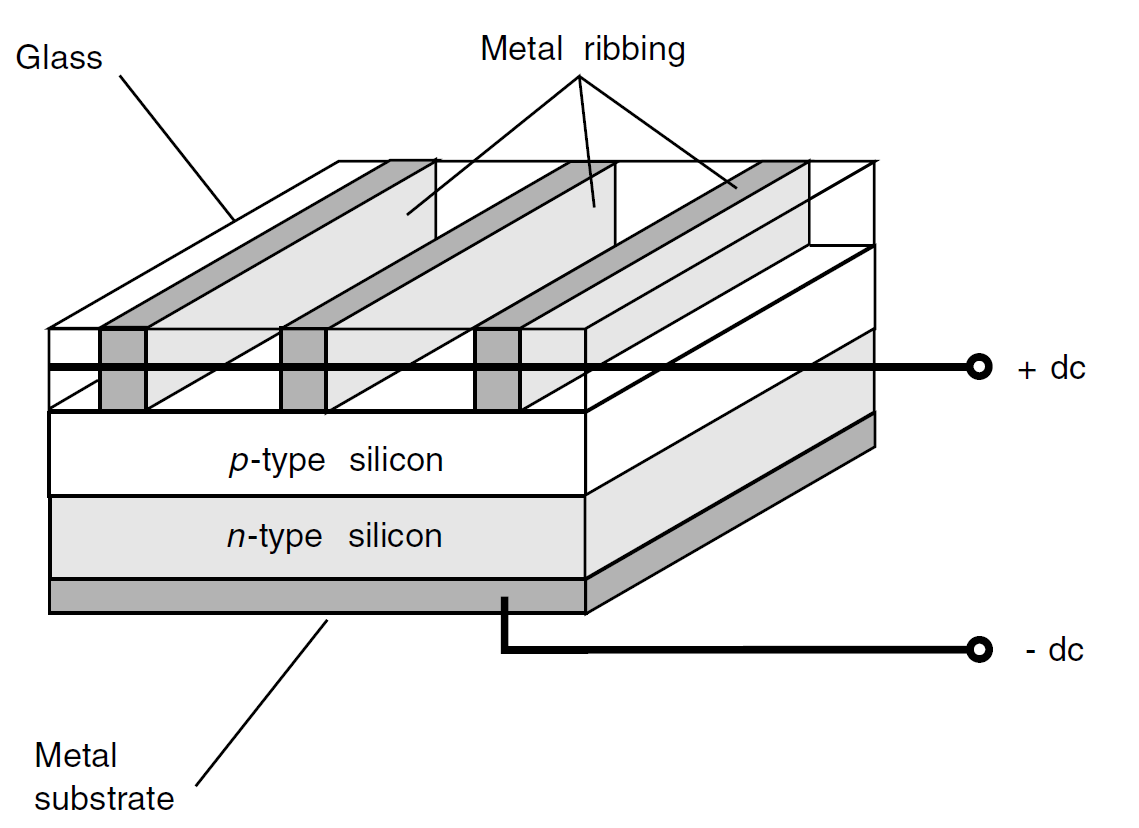
Fig. 1. Simplified cross-sectional drawing of a photovoltaic (PV) cell.