

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
X-ray : Rotating Crystal Method
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
10-4-2020
3257
X-ray : Rotating Crystal Method
To describe the periodic, three dimensional nature of crystals, the Laue equations are employed:
where a, b, and c are the three axes of the unit cell, θo, o, ?o are the angles of incident radiation, and ?, ?, ? are the angles of the diffracted radiation. A diffraction signal (constructive interference) will arise when h, k, and l are integer values. The rotating crystal method employs these equations. X-ray radiation is shown onto a crystal as it rotates around one of its unit cell axis. The beam strikes the crystal at a 90 degree angle. Using equation 1 above, we see that if θo is 90 degrees, then cosθo=0. For the equation to hold true, we can set h=0, granted that heta= 90. The above three equations will be satisfied at various points as the crystal rotates. This gives rise to a diffraction pattern (shown in the image below as multiple h values). The cylindrical film is then unwrapped and developed. The following equation can be used to determine the length axis around which the crystal was rotated:
where a is the length of the axis, y is the distance from h=0 to the h of interest, r is the radius of the firm, and ? is the wavelength of the x-ray radiation used. The first length can be determined with ease, but the other two require far more work, including remounting the crystal so that it rotates around that particular axis.
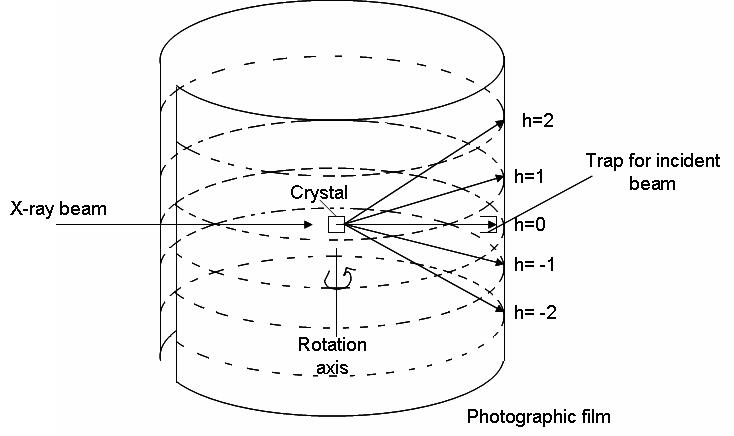
Figure 1:
 الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















