

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Hydrides E2H4 (E=N, P, As)
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 397
16-2-2018
2593
Hydrides E2H4 (E=N, P, As)
Hydrazine, N2H4, is a colourless liquid (mp 275 K, bp 386 K), miscible with water and with a range of organic solvents, and is corrosive and toxic; its vapour forms explosive mixtures with air. Although ΔfHo(N2H4, 298 K)= 50.6 kJ mol-1, N2H4 at ambient temperatures is kinetically stable with respect to N2 and H2. Alkyl derivatives of hydrazine have been used as rocket fuels, e.g. combined with N2O4 in the Apollo missions. N2H4 has uses in the agricultural and plastics industries, and in the removal of O2 from industrial water boilers to minimize corrosion (the reaction gives N2 and H2O). Hydrazine is obtained by the Raschig reaction (the basis for the industrial synthesis) which involves the partial oxidation of NH3 .
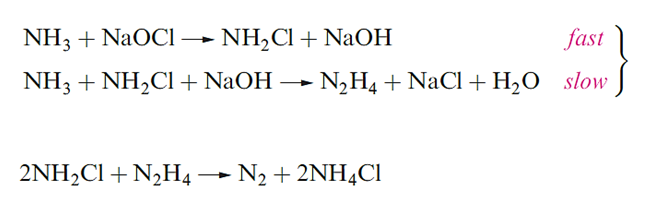
Hydrazine is obtained from the Raschig process as the monohydrate and is used in this form for many purposes. Dehydration is difficult, and direct methods to produce anhydrous N2H4 include reaction below.
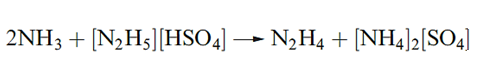
In aqueous solution, N2H4 usually forms [N2H5]+ (hydrazinium) salts, but some salts of [N2H6]2+ have been isolated, e.g. [N2H6][SO4]. The pKb values for hydrazine are given in equations below and the first step shows N2H4 to be a weaker base than NH3 .
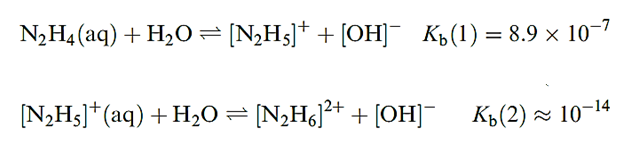
Both N2H4 and [N2H5] are reducing agents, and used for the determination of hydrazine.
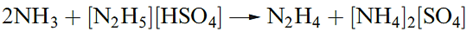
We have alreadymentioned the use of N2H4 in rocket fuels. The stored energy in explosives and propellants (‘high energy density materials’) usually arises either from oxidation of an organic framework, or from an inherent high positive enthalpy of formation. For the hydrazinium salt [N2H5]2[14.15] ΔfHo(s,298 K)= 858 kJ mol-1 (or 3.7 kJ g-1), making [N2H5]2[14.15] a spectacular example of a high energy density material.
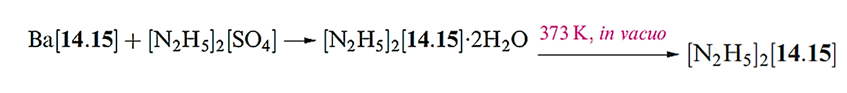
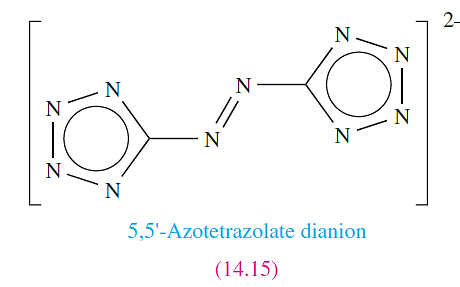
Figure 1.1a shows the structure of N2H4, and the gauche conformation is also adopted by P2H4 in the gas phase.
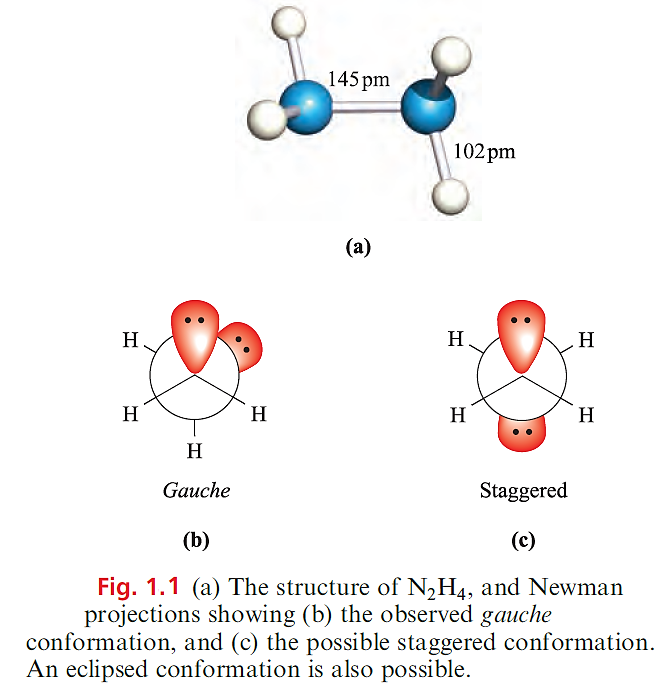
In the solid state, P2H4 has a staggered conformation (Figure 1.1c) while the related N2F4 exhibits both conformers. The eclipsed conformation (which would maximize lone pair–lone pair repulsions) is
not observed. Diphosphane, P2H4, is a colourless liquid (mp 174 K, bp 329 K), and is toxic and spontaneously inflammable; when heated, it forms higher phosphanes. Diphosphane is formed as a minor product in several reactions in which PH3 is prepared and may be separated
from PH3 by condensation in a freezing mixture. It exhibits no basic properties. The [P3H3]2- ion is formed in reaction 14.38 and is stabilized by coordination to the sodium centre in [Na(NH3)3(P3H3)]-. In the solid state, the H atoms in [P3H3]2- are in an all-trans configuration .
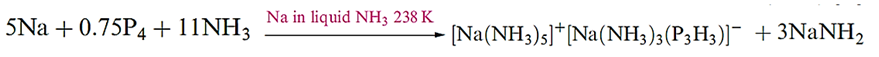
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















