
Uses of group 14 elements
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 339
الجزء والصفحة:
p 339
 1-2-2018
1-2-2018
 1443
1443
Uses of group 14 elements
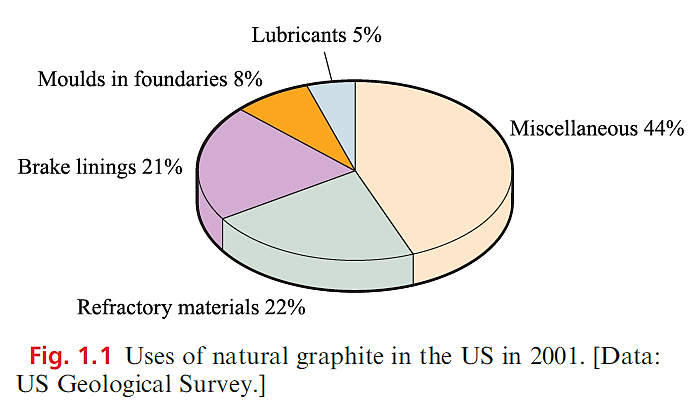
Diamond is the hardest known substance, and apart from its commercial value as a gemstone, it has applications in cutting tools and abrasives. The structural differences between diamond and graphite lead to remarkable differences in physical properties and uses. The properties of graphite that are exploited commercially (see Figure 1.1) are its inertness, high thermal stability, electrical and thermal conductivities and ability to act as a lubricant. Its thermal and electrical properties make graphite suitable as a refractory material and for uses in batteries and fuel cells. The growing importance of fuel-cell technology will result in a growth in demand for high-purity graphite.
Other new technologies are having an impact on the market for graphite. For example, graphite cloth (،flexible graphite’) is a relatively new product and applications are increasing. Charcoal (made by heating wood) and animal charcoal (produced by charring treated bones) are microcrystalline forms of graphite, supported, in the case of animal charcoal, on calcium phosphate. The adsorption properties of activated charcoal render it commercially important. Carbon fibres of great tensile strength (formed by heating oriented organic polymer fibres at ≥1750 K) contain graphite crystallites oriented parallel to the fibre axis, and are used to strengthen materials such as plastics. Carbon-composites are fibre-reinforced, chemically inert materials which possess high strength, rigidity, thermal stability, high resistance to thermal shock and retain their mechanical properties at high temperature. Such properties have led to their use in external body parts of the space shuttle.
Silicon has major applications in the steel industry and in the electronic and semiconductor industries. Silica, SiO2, is an extremely important commercial material; it is the main component of glass, and large quantities of sand are consumed worldwide by the building industry. Quartz glass (formed on cooling fused SiO2) can withstand sudden temperature changes and has specialist uses. Silica gel (an amorphous form of silica, produced by treating aqueous sodium silicate with acid) is used as a drying agent, a stationary phase in chromatography, and a heterogeneous catalyst. Caution! Inhalation of silica dusts may lead to the lung disease silicosis. Hydrated silica forms the exoskeletons of marine diatoms, but the role of Si in other biological systems is less well defined.
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


