
Beryllium halides
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 280
الجزء والصفحة:
p 280
 19-1-2018
19-1-2018
 2082
2082
Beryllium halides
Anhydrous beryllium halides are covalent. The fluoride, BeF2, is obtained as a glass (sublimation point 1073 K) from the thermal decomposition of [NH4]2[BeF4], itself prepared from BeO and NH3 in an excess of aqueous HF. Molten BeF2 is virtually a non-conductor of electricity, and the fact that solid BeF2 adopts a b-cristobalite lattice is consistent with its being a covalent solid. Beryllium difluoride is very soluble in water, the formation of [Be(H2O)4] 2+ being thermodynamically favourable. This is a standard method of preparing a metal chloride that cannot be made by dehydration of hydrates obtained from aqueous media. In the case of Be, [Be(H2O)4] 2+ is formed and attempted dehydration of [Be(H2O)4]Cl2 yields the hydroxide, not the chloride.
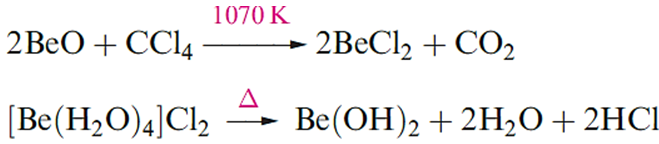
A deliquescent substance absorbs water from the surrounding air and eventually forms a liquid. In the vapour state above 1020 K, BeCl2 is monomeric and has a linear structure; at lower temperatures, the vapour also contains planar dimers. We return to the structures of gasphase BeX2 molecules later in the section. It forms colourless, deliquescent crystals containing infinite chains; the coordination environment of each Be centre is tetrahedral and the Be–Cl distances are longer than in the monomer (Figure 1.1).

In the polymer, each Be atom can be considered to be sp3 hybridized and a localized s-bonding scheme is appropriate in which each Cl donates a lone pair of electrons into an empty hybrid orbital on an adjacent Be atom (Figure 1.1c). The formation of this chain demonstrates the Lewis acidity of beryllium dihalides; BeCl2 acts as a Friedel–Crafts catalyst (i.e. like AlCl3), and the formation of adducts is illustrated by [BeF4]2-, [BeCl4]2- and BeCl2.2L (L= ether, aldehyde, ketone). and a localized s-bonding scheme is appropriate in which each Cl donates a lone pair of electrons into an empty hybrid orbital on an adjacent Be atom (Figure 1.1c). The formation of this chain demonstrates the Lewis acidity of beryllium dihalides; BeCl2 acts as a Friedel–Crafts catalyst (i.e. like AlCl3), and the formation of adducts is illustrated by [BeF4]2-, [BeCl4]2- and BeCl2.2L (L= ether, aldehyde, ketone).
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


