

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Weight Average MolecularWeight
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 319
20-9-2017
1096
Weight Average MolecularWeight
The weight average molecular weight (Mw) is the sum of the products of the weight of each species present and its molecular weight, divided by the sum of all the species’ weights:
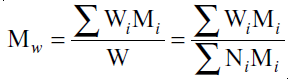
Wi = weight of each polymeric species
Mi = molecular weight of each polymeric species
Substituting NiMi = Wi, the weight average molecular weight can be defined as Larger, heavier molecules contribute more to Mw than to Mn. Light scattering techniques and ultracentrifugation can determine Mw.
The following simple example illustrates the difference between Mn and Mw: Suppose a sample has six macro-molecules. Three of them have a molecular weight = 1.0 × 104, two have a molecular weight = 2.0 × 104, and one has a molecular weight = 3.0 × 104:
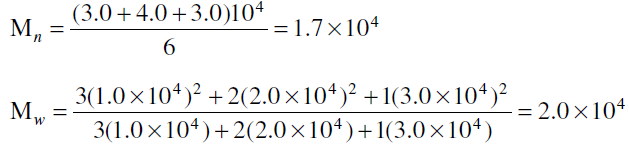
In monodispersed systems Mn = Mw.
The difference in the value between Mn and Mw. indicates the polydispersity of the polymer system. The closer Mn is to Mw, the narrower the molecular weight spread. Molecular weight distribution curves for polydispersed systems can be obtained by plotting the degree of polymerization i versus either the number fraction, Ni, or the weight fraction, Wi.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء البوليمرات
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء البوليمرات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















