

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
MONOMERS, POLYMERS, AND COPOLYMERS
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 302
14-9-2017
1953
MONOMERS, POLYMERS, AND COPOLYMERS
A monomer is a reactive molecule that has at least one functional group (e.g. -OH, -COOH, -NH2, -C=C-). Monomers may add to themselves as in the case of ethylene or may react with other monomers having different functionalities. A monomer initiated or catalyzed with a specific catalyst polymerizes and forms a macromolecule—a polymer.
For example, ethylene polymerized in presence of a coordination catalyst produces a linear homopolymer (linear polyethylene):
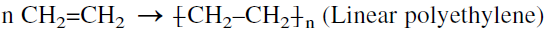
A copolymer, on the other hand, results from two different monomers by addition polymerization. For example, a thermoplastic polymer with better properties than an ethylene homopolymer comes from copolymerizing ethylene and propylene:
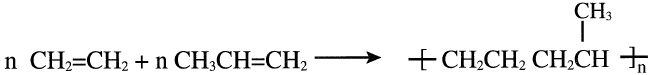
Block copolymers are formed by reacting two different prepolymers, which are obtained by polymerizing the molecules of each monomer separately. A block copolymer made of styrene and butadiene is an important synthetic rubber:
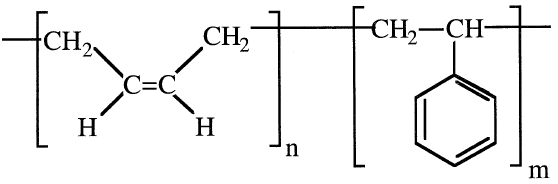
Alternating copolymers have the monomers of one type alternating in a regular manner with the monomers of the other, regardless of the composition of the reactants. For example, an alternate copolymer of vinyl acetate and vinyl chloride could be represented as:
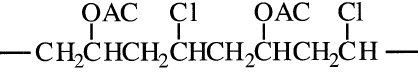
Random copolymers have the different monomer molecules distributed randomly along the polymer chain.
A polymer molecule may have just a linear chain or one or more branches protruding from the polymer backbone. Branching results mainly from chain transfer reactions and affects the polymer’s physical and mechanical properties. Branched polyethylene usually has a few long branches and many more short branches
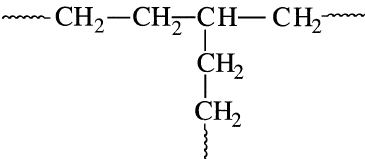
Intentional branching may improve the properties of the product polymer through grafting. A graft copolymer can be obtained by creating active sites on the polymer backbone. The addition of a different monomer then reacts at the active site and forms a branch. For example, polyethylene irradiated with gamma rays and then exposed to a reactive monomer, such as acrylonitrile, produces a polyethylene-polymer with acrylonitrile branches:
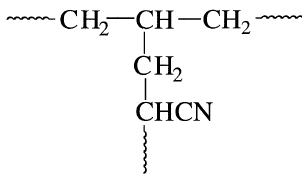
Crosslinked polymers have two or more polymer chains linked together at one or more points other than their ends. The network formed improves the mechanical and physical properties of the polymer. Crosslinking may occur during the polymerization reaction when multifunctional groups are present (as in phenol-formaldehyde resins) or through outside linking agents (as in the vulcanization of rubber with sulfur).
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















