

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Styrene
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 266
10-9-2017
4318
Styrene
Styrene (vinylbenzene) is a liquid (b.p. 145.2°C) that polymerizes easily when initiated by a free radical or when exposed to light. The 1998 U.S. production of styrene was approximately 11 billion pounds. Dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene to styrene occurs over a wide variety of metal oxide catalysts. Oxides of Fe, Cr, Si, Co, Zn, or their mixtures can be used for the dehydrogenation reaction. Typical reaction conditions for the vapor-phase process are 600–700°C, at or below atmospheric pressure. Approximately 90% styrene yield is obtained at 30–40% conversion:
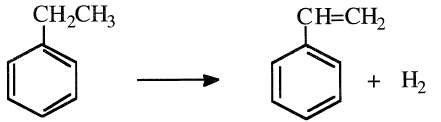
In the Monsanto/Lummus Crest process (Figure 1.1), fresh ethylbenzene with recycled unconverted ethylbenzene are mixed with superheated steam. The steam acts as a heating medium and as a diluent. The endothermic reaction is carried out in multiple radial bed reactors filled with proprietary catalysts. Radial beds minimize pressure drops across the reactor. A simulation and optimization of styrene plant based on the Lummus
Monsanto process has been done by Sundaram et al. Yields could be predicted, and with the help of an optimizer, the best operating conditions can be found. Figure 1.2 shows the effect of steam-to-EB ratio, temperature, and pressure on the equilibrium conversion of ethylbenzene.
Alternative routes for producing styrene have been sought. One approach is to dimerize butadiene to 4-vinyl-1-cyclohexene, followed by catalytic dehydrogenation to styrene
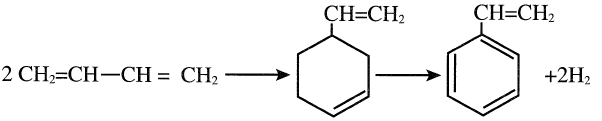
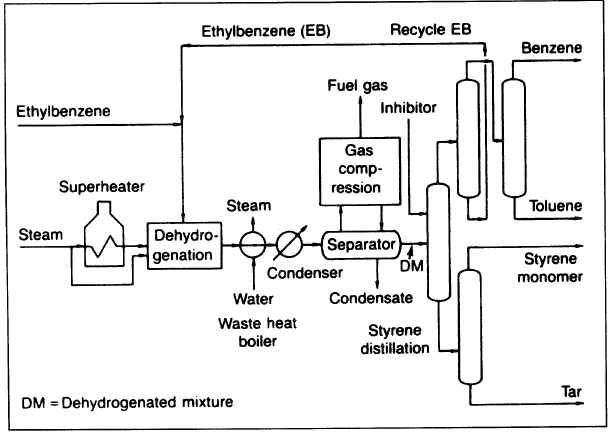
Figure 1.1. Schematic diagram of the Monsanto/Lummus Crest styrene plant.
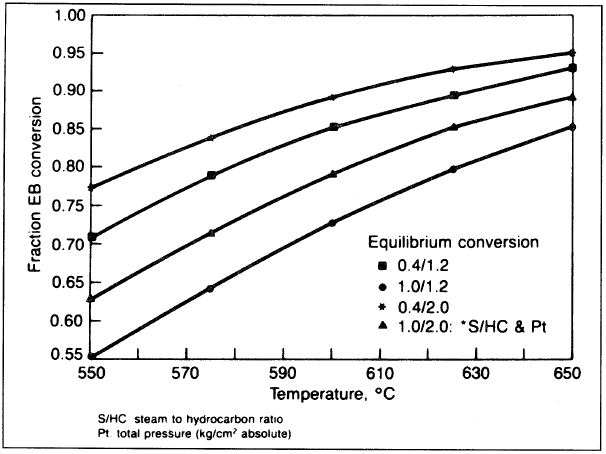
Figure 1.2. Effect of steam/EB, temperature, and pressure on the conversion of ethylbenzene.
The process which was developed by DOW involves cyclodimerization of butadiene over a proprietary copper-loaded zeolite catalyst at moderate temperature and pressure (100°C and 250 psig). To increase the yield, the cyclodimerization step takes place in a liquid phase process over the catalyst. Selectivity for vinylcyclohexene (VCH) was over 99%. In the second step VCH is oxidized with oxygen over a proprietary oxide catalyst in presence of steam. Conversion over 90% and selectivity to styrene of 92% could be achieved.
Another approach is the oxidative coupling of toluene to stilbene followed by disproportionation to styrene and benzene:
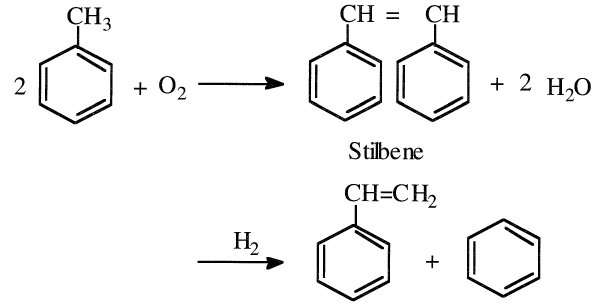
High temperatures are needed for this reaction, and the yields are low.
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















