
Ethylene Glycol (CH2OHCH2OH)
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 192
الجزء والصفحة:
p 192
 22-8-2017
22-8-2017
 3126
3126
Ethylene Glycol (CH2OHCH2OH)
Ethylene glycol (EG) is colorless syrupy liquid, and is very soluble in water. The boiling and the freezing points of ethylene glycol are 197.2° and –13.2°C, respectively.
Current world production of ethylene glycol is approximately 15 billion pounds. Most of that is used for producing polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resins (for fiber, film, bottles), antifreeze, and other products. Approximately 50% of the world EG was consumed in the manufacture of polyester fibers and another 25% went into the antifreeze. EG consumption in the US was nearly 1/3 of the world's. The use pattern, however, is different; about 50% of EG is consumed in antifreeze.
The US production of ethylene glycol was 5.55 billion pounds in 1994, the 30th largest volume chemical.
The main route for producing ethylene glycol is the hydration of ethylene oxide in presence of dilute sulfuric acid (Figure 1.1):
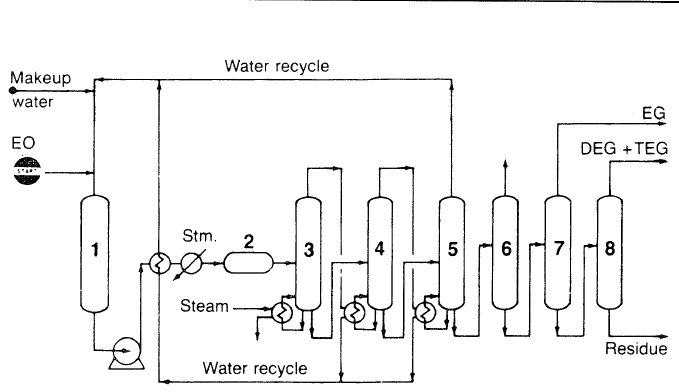
Figure 1.1. The Scientific Design Co. process for producing ethylene glycols from ethylene oxide:5 (1) feed tank, (2) reactor, (3,4,5) multiple stage evaporators, #4 operates at lower pressure than #3, while #5 operates under vacuum, evaporated water is recycled to feed tank, (6) light ends stripper, (7,8) vacuum distillation columns.
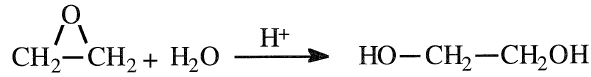
The hydrolysis reaction occurs at a temperature range of 50–100°C. Contact time is approximately 30 minutes. Di- and triethylene glycols are coproducts with the monoglycol. Increasing the water/ethylene oxide ratio and decreasing the contact time decreases the formation of higher glycols. A water/ethylene oxide ratio of 10 is normally used to get approximately 90% yield of the monoglycol. However, the di- and the triglycols are not an economic burden, because of their commercial uses.
A new route to ethylene glycol from ethylene oxide via the intermediate formation of ethylene carbonate has recently been developed by Texaco. Ethylene carbonate may be formed by the reaction of carbon monoxide, ethylene oxide, and oxygen. Alternatively, it could be obtained by the reaction of phosgene and methanol.
Ethylene carbonate is a reactive chemical. It reacts smoothly with methanol and produces ethylene glycol in addition to dimethyl carbonate:
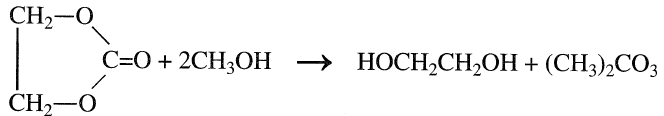
The reaction occurs at approximately 80–130°C using the proper catalyst. Many catalysts have been tried for this reaction, and there is an indication that the best catalyst types are those of the tertiary amine and uaternary ammonium functionalized resins. This route produces ethylene glycol of a high purity and avoids selectivity problems associated with the hydrolysis of ethylene oxide.
The coproduct dimethyl carbonate is a liquid soluble in organic solvents. It is used as a specialty solvent, a methylating agent in organic synthesis, and a monomer for polycarbonate resins. It may also be considered as a gasoline additive due to its high oxygen content and its high octane rating.
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


