

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Oxidation Numbers
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المصدر:
College Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 84
12-7-2017
1946
Oxidation Numbers
The degree of oxidation of an element is specified by the atom's oxidation number (ON), rules for which are as follows:
1. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion, e.g., for Fe2+, ON(Fe) = +2, for Cl-, ON(Cl) = -1. The alkali metals (Group IA) and alkaline earth metals (Group IIA) are always ionic in compounds like NaCl or Mg(NO3)2.
2. The ON of an uncombined element is 0, e.g., the ON is 0 for H in H2(g), S in S8(s).
3. The following conventions apply to covalently bound atoms: Except for the elements, (a) ON(F) = -1 (always); (b) ON(O) = -2 (except in peroxides like HOOH, where ON(O) = -1); (c) ON (H) = +1 (except in metal hydrides like NaH, where ON(H) = -1).
4. In molecules or ions containing two or more atoms, the sum of the ONs of all the atoms equals the charge on the species, e.g., H2O: ON(O) + 2 ON(H) = -2 + 2(+1) = 0; to find ON(N) in NO3-: ON(N) + 3
ON(O) = -1, thus ON(N) = -1 -3(-2) = +5.
Example 1
What is the oxidation number of P in PO43-?
In PO43- , rule (4) gives
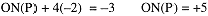
Example 2
What is the oxidation number of Si in H2SiO3?
In H2SiO3, rule (4) gives:
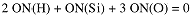
With rules (3b) and (3c), we have
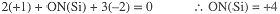
It is important to recognize that oxidation numbers are a book-keeping device and should not be takento indicate true charges or even formal charges. In H2SiO3—SiO(OH)2—the Si-O and O-H bonds are covalent, i.e., electrons are shared between atoms; although we might expect the Si and H atoms to be somewhat positive and the O atoms somewhat negative, the charge separation is nowhere near as great as suggested by the ONs.
 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















