

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
COORDINATION POLYMERIZATION
المؤلف:
Robert O. Ebewele
المصدر:
POLYMER SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
الجزء والصفحة:
P 46
22-6-2017
889
COORDINATION POLYMERIZATION
As we shall see in Chapter 4, monomers with side groups asymmetrically disposed with respect to the double bond are capable of producing polymers in which the side groups have a specific stereochemical or spatial arrangement (isotactic or syndiotactic). In both cationic and anionic polymerizations, the association of initiating ion and counterion permits a preferential placement of asymmetric substituted monomers, the extent of which depends on the polymerization conditions. Unbranched and stereospecific polymers are also produced by the use of Ziegler–Natta catalysts. These are complex catalyst systems derived from a transition metal compound from groups IVB to VIIIB of the periodic table and an organometallic compound usually from a group IA or IIIA metal. A typical catalyst complex is that formed by trialkyl aluminum and titanium trichloride as shown below:
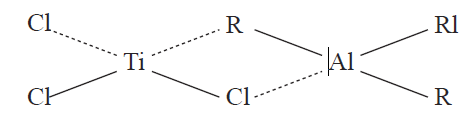
Monoolefins such as propylene and dienes such as butadiene and isoprene can be polymerized using Ziegler–Natta coordination catalysts. The catalysts function by forming transient π -complexes between the monomers and the transition metal species. The initiating species is a metal–alkyl complex and propagation involves the consecutive insertion of monomer molecules into a polarized titanium–carbon bond. Coordination polymerizations may be terminated by introducing poisons such as water, hydrogen, aromatic alcohols, or metals like zinc into the reacting system.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء البوليمرات
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء البوليمرات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















