

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Terpenes: Naturally Occurring Alkenes
المؤلف:
John McMurry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 257
23-5-2017
4108
Terpenes: Naturally Occurring Alkenes
Ever since its discovery in Persia around 1000 a.d., it has been known that steam distillation, the codistillation of plant materials with water, produces a fragrant mixture of liquids called essential oils. The resulting oils have long been used as medicines, spices, and perfumes, and their investigation played a major role in the emergence of organic chemistry as a science during the 19th century.
Chemically, plant essential oils consist largely of mixtures of compounds called terpenoids—small organic molecules with an immense diversity of structure. More than 35,000 different terpenoids are known. Some are open-chain molecules, and others contain rings; some are hydrocarbons, and others contain oxygen. Hydrocarbon terpenoids, in particular, are known as terpenes, and all contain double bonds. For example:
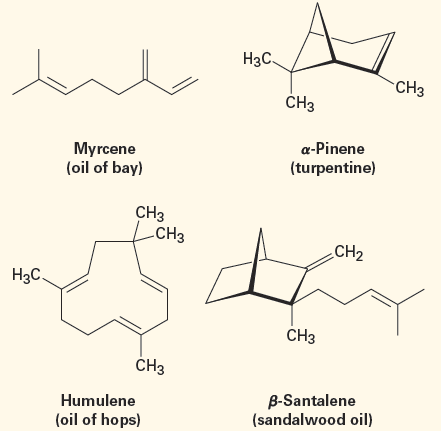
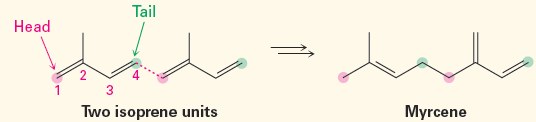
Regardless of their apparent structural differences, all terpenoids are related. According to a formalism called the isoprene rule, they can be thought of as arising from head-to-tail joining of 5-carbon isoprene units (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene). Carbon 1 is the head of the isoprene unit, and carbon 4 is the tail. For example, myrcene contains two isoprene units joined head to tail, forming an 8-carbon chain with two 1-carbon branches. a-Pinene similarly contains two isoprene units assembled into a more complex cyclic structure, and humulene contains three isoprene units. See if you can identify the isoprene units in a-pinene, humulene, and b-santalene.
Terpenes (and terpenoids) are further classified according to the number of 5-carbon units they contain. Thus, monoterpenes are 10-carbon substances derived from two isoprene units, sesquiterpenes are 15-carbon molecules derived from three isoprene units, diterpenes are 20-carbon substances derived from four isoprene units, and so on. Monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes are found primarily in plants, but the higher terpenoids occur in both plants and animals, and many have important biological roles. The triterpenoid lanosterol, for instance, is the biological precursor from which all steroid hormones are made.
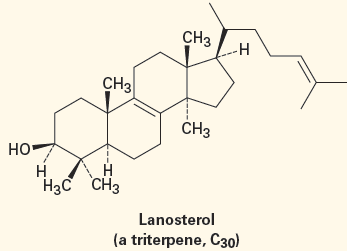
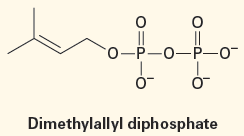
Isoprene itself is not the true biological precursor of terpenoids. Nature instead uses two “isoprene equivalents”—isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate—which are themselves made by two different routes depending on the organism. Lanosterol, in particular, is biosynthesized from acetic acid by a complex pathway that has been worked out in great detail.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















