

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Major uses of the group 13 elements and their compounds
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 358
5-4-2017
2216
Major uses of the group 13 elements and their compounds
The widespread applications of Al are summarized in Figure 1.1a; its strength can be increased by alloying with Cu or Mg. Aluminium oxide has many important uses. Corundum (a-alumina) and emery (corundum mixed with the iron oxides magnetite and haematite) are extremely hard and are used as abrasives; diamond is the only naturally occurring mineral harder than corundum.
Gemstones including ruby, sapphire, oriental topaz, oriental amethyst and oriental emerald result from the presence of trace metal salts in Al2O3, e.g. Cr(III) produces the red colour of ruby. Artificial crystals can be manufactured from bauxite in furnaces, and artificial rubies are important as components in lasers. The g-form of Al2O3 is used as a catalyst and as a stationary phase in chromatography. Al2O3 fibres are described in Section 27.7.

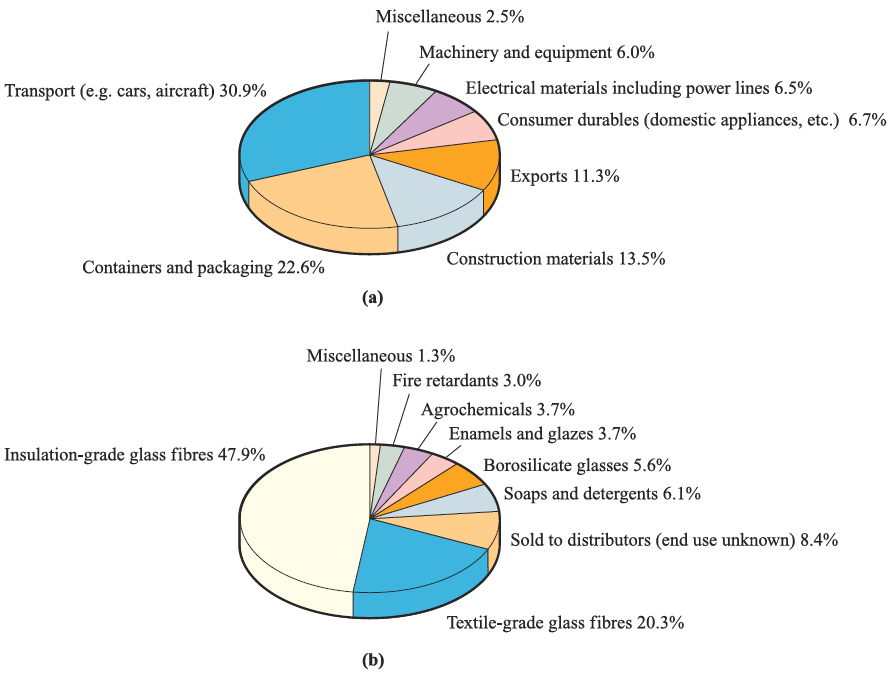
Fig. 1.1 (a) Uses of aluminium in the US in 2001; the US is the world’s largest producer of the metal and in 1990, a quarter of that manufactured was exported. (b) Uses of boron in the US in 2001; the data are given in terms of tonnes of boron oxide content. [Data: US Geological Survey.]
The two commercially most important borates are Na2 [B4O5(OH)4]. 8H2O (borax) and Na2 [B4O5(OH)4]. 2H2O (kernite). Figure 1.1b illustrates the applications of boron (in terms of boron oxide usage). Borosilicate glass has a high refractive index and is suitable for optical lenses. Borax has been used in pottery glazes for many centuries and remains in use in the ceramics industry. The reaction between fused borax and metal oxides is the basis for using borax as a flux in brazing; when metals are being fused together, coatings of metal oxides must be removed to ensure good metal–metal contact at the point of fusion.
Boric acid, B(OH)3, is used on a large scale in the glass industry, as a flame retardant (see Box 16.1), as a component in buffer solutions and is also an antibacterial agent. The use of B2O3 in the glass industry is described in Box 12.5.
Elemental boron is used in the production of impactresistant steels and (because 10B has a high cross-section for neutron capture) in control rods for nuclear reactors. Amorphous B is used in pyrotechnics, giving a characteristic green colour when it burns.
Gallium and indium phosphides, arsenides and antimonides have important applications in the semiconductor industry. They are used as transistor materials and in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in, for example, pocket calculators; the colour of the light emitted depends on the band gap. Figure 1.1 shows that, in 2001, the US used 37% of the gallium produced worldwide.

Fig. 1.1 World production and US consumption of gallium between 1975 and 2001. [Data: US Geological Survey.]
Almost all of this was used in the form of GaAs: 34% went into LEDs, laser diodes, photodetectors and solar cells, while 65% found application in integrated circuits, e.g. in high-performance computers. (Miscellaneous uses, including research and development, account for the remaining 1%.) Markets linked to the electronics industry are susceptible to fluctuation depending on world or local economies. This is apparent in Figure 1.1 where the decrease in demand for gallium (specifically GaAs) in the US between 2000 and 2001 can be attributed to a drop in sales of mobile phones. The largest use of indium is in thin-film coatings, e.g. liquid-crystal displays and electroluminescent lamps; in 2002, these applications accounted for 45% of the indium used in the US. Indium is also used in lead-free solders, in semiconductors, for producing seals between glass, ceramics and metals (because In has the ability to bond to non-wettable materials), and for fabricating special mirrors which reduce headlight glare. Uses of indium–tin oxide (ITO) are highlighted in.
Thallium sulfate used to be used to kill ants and rats, but the extremely high toxicity levels of Tl compounds are now well recognized and all Tl-containing species must be treated with caution. The world production of thallium (15 000 kg in 2001) is far less than that of gallium (Figure 1.1) and indium. Important uses of Tl are in semiconducting materials in selenium rectifiers, in Tl-activated NaCl and NaI crystals in γ-radiation detectors, and in IR radiation detection and transmission equipment. The radioisotope 201Tl (t1/2= 12.2 d) is used for cardiovascular imaging.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















