

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
SO2 and sulfites in wine
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 457
21-3-2017
1987
SO2 and sulfites in wine
During the fermentation process in the manufacture of wine, SO2 or K2S2O5 is added to the initial wine pressings to kill microorganisms, the presence of which results in spoilage of the wine. Molecular SO2 is only used for large scale wine production, while K2S2O5 is the common additive in small scale production. In acidic solution, [S2O5]2- undergoes the following reactions:
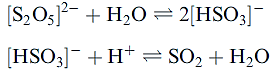
The overall equilibrium system for aqueous SO2 is:
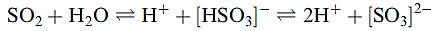
The position of equilibrium is pH-dependent; for the fermentation process, the pH is in the range 2.9–3.6. Only molecular SO2 is active against microorganisms. The first (i.e. yeast) fermentation step is followed by a bacterial fermentation step (malolactic fermentation) in which malic acid is converted to lactic acid. After this stage, SO2 is added to stabilize the wine against oxidation. Adding SO2 too early destroys the bacteria that facilitate malolactic fermentation. Malolactic fermentation is usually only important in red wine production. The addition of SO2 to white and red wines is handled differently. Red wines contain anthocyanin pigments, and these react with [HSO3]- or [SO3]2- resulting in a partial loss of the red coloration. Clearly, this must be avoided and means that addition of SO2 to red wine must be carefully controlled. On the other hand, significantly more SO2 can be added to white wine. Red wine, therefore, is less well protected by SO2 against oxidation and spoilage by microorganisms than white wine, and it is essential to ensure that sugar and malic acid (food for the microbes) are removed from red wine before bottling. Red wine does possess a higher phenolic content than white wine, and this acts as a built-in anti-oxidant.
Wines manufactured in the US carry a ‘contains sulfites’ statement on the label. Some people are allergic to sulfites, and one possible substitute for SO2 is the enzyme lysozyme. Lysozyme attacks lactic bacteria, and is used in cheese manufacture. However, it is not able to act as an antioxidant.
A possible solution (not yet adopted by the wine industry) would be to mount a combined offensive: adding lysozyme and a reduced level of SO2.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















