

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
xenone Oxides
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 499
4-3-2017
1451
xenone Oxides
Equations 1.1 and 1.2 showed the formation of XeO3 by hydrolysis of XeF4 and XeF6. Solid XeO3 forms colourless crystals and is dangerously explosive (∆fHo)298K(= 402 kJ mol-1). The solid contains trigonal pyramidal molecules (1.1). Xenon trioxide is only weakly acidic and its aqueous solution is virtually non-conducting. Reactions of XeO3 and MOH (M = K, Rb, Cs) produce xenates (equation 1.3) which slowly disproportionate in olution (equation 1.4).
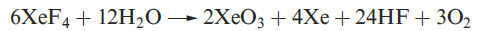 (1.1)
(1.1)
 (1.2)
(1.2)
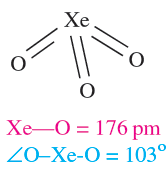
(1.1)
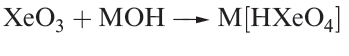 (1.3)
(1.3)
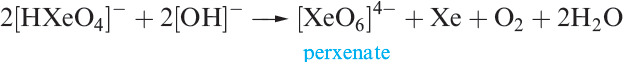 (1.4)
(1.4)
Aqueous [XeO6]4- is formed when O3 is passed through a dilute solution of XeO3 in alkali. Insoluble salts such as Na4XeO6.8H2O and Ba2XeO6 may be precipitated, but perxenic acid ‘H4XeO6 (a weak acid in aqueous solution) has not been isolated. The perxenate ion is a powerful oxidant and is rapidly reduced in aqueous acid (equation 1.5); oxidations such as Mn(II) to [MnO4]- occur instantly in acidic media at 298 K.
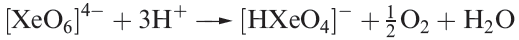 (1.5)
(1.5)
Xenon tetraoxide is prepared by the slow addition of concentrated H2SO4 to Na4XeO6 or Ba2XeO6. It is a pale yellow, highly explosive solid (∆fHo(298K) = 642 kJ mol-1) which is a very powerful oxidizing agent. Tetrahedral XeO4 molecules (1.3) are present in the gas phase.
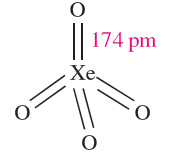
(1.3)
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















